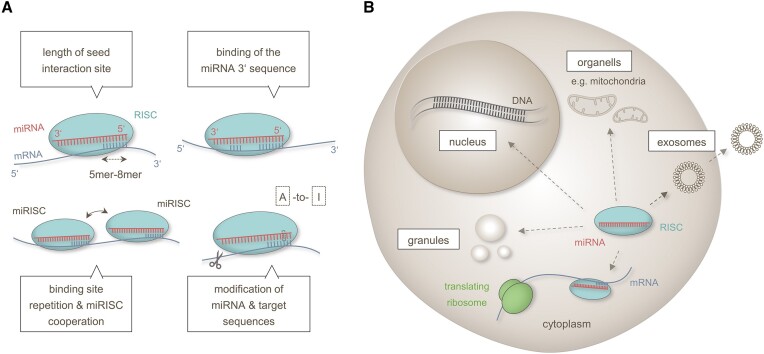
Figure 2.
Overview on miRNA–target bindings and miRNA localization changes. (A) The regulatory capacity of MTIs is a function of the length of binding interaction between the miRNA seed sequence and the mRNA target, the presence of 3′ binding sites, the cooperation between multiple miRNA-responsive elements and the modification of both, the miRNAs and target sequences through e.g. A-to-I RNA editing or 3′UTR shortening. (B) Intra-cellular miRNA sub-localizations include membranous comparts like the nucleus or mitochondria and non-membranous comparts like granules. Extracellular miRNA localization can result from secretion of vesicles like exosomes. [MiRNAs are indicated as red lines, mRNAs as blue lines, interactions between miRNA and mRNA by opposite comb-shaped lines. Length variations are depicted by dashed two-sided arrows and translocations by solid two-sides arrows. Ribosomes are shown as green bodies, RISC as turquoise bodies. Sequence shortening is symbolized by cutting scissors and sequence exchanges by dotted rectangles.]