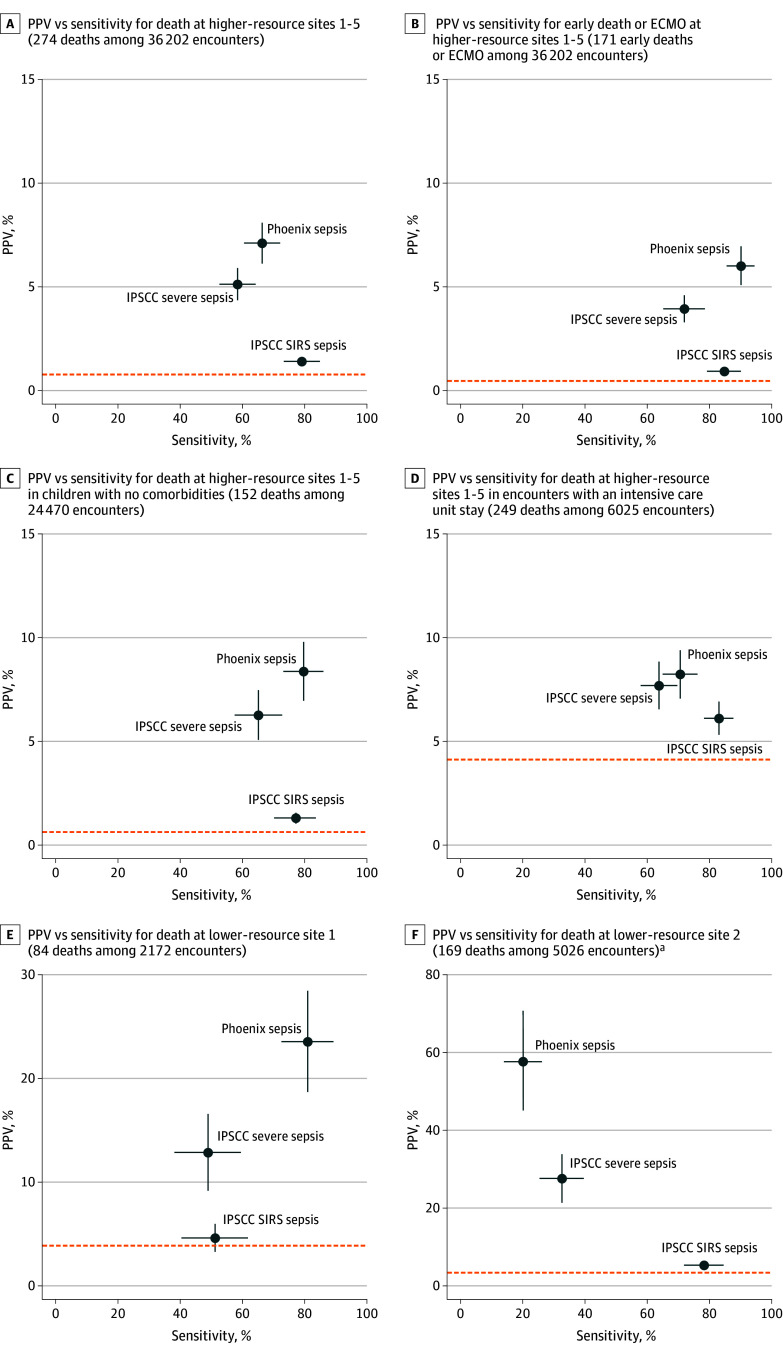
Figure 4. Comparison of Sensitivity and PPV of Novel Phoenix Sepsis Criteria With Current IPSCC Sepsis and Severe Sepsis Criteria Across Outcomes and Patient Subgroups in the Internal Validation Sets.
The positive predictive value (PPV, or precision) and sensitivity for the Phoenix vs 2005 International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference (IPSCC) criteria for sepsis in children with suspected infection are shown. The Phoenix sepsis criteria are based on achieving ≥2 points in the Phoenix Sepsis Score among patients with suspected infection in the first 24 hours of an encounter. The IPSCC sepsis and severe sepsis criteria are based on systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and IPSCC-based organ dysfunction among patients with suspected infection in the first 24 hours of an encounter. Baseline rates of the outcome in each group (death, or early death or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO]) are shown as horizontal dashed lines. 95% CIs are shown as bands from each point in the plane representing that component (eg, CIs for PPV are parallel to the y-axis). Confidence bands that are not visible are narrow enough to be completely hidden by the point. These figures are similar to area under the precision recall curves except at a single threshold for criteria that generate a binary response (eg, yes/no sepsis criteria met) instead of across the range of possible points in the curve (eg, 0-13 points in the Phoenix Sepsis Score; see Figure 3). Better-performing criteria are closer to the top right corner. A trade-off exists between sensitivity and PPV, with more sensitive criteria usually having lower PPV and more specific criteria usually having higher PPV and lower sensitivity. Criteria that are close to the baseline outcome rate have poor predictive value.
aAt lower-resource site 2, some Phoenix Sepsis Score and IPSCC data inputs (eg, invasive mechanical ventilation, Glasgow Coma Scale score) are not recorded even when they are performed; thus, assessment of criteria performance is limited. Lower-resource site 1 and all higher-resource sites have inputs for all relevant organ systems in the criteria. Comparison of sepsis criteria in the external validation sites is shown in eFigure 10 in Supplement 1 with similar results. Diagnostic performance measures for this comparison are shown in eTable 7 in Supplement 1.