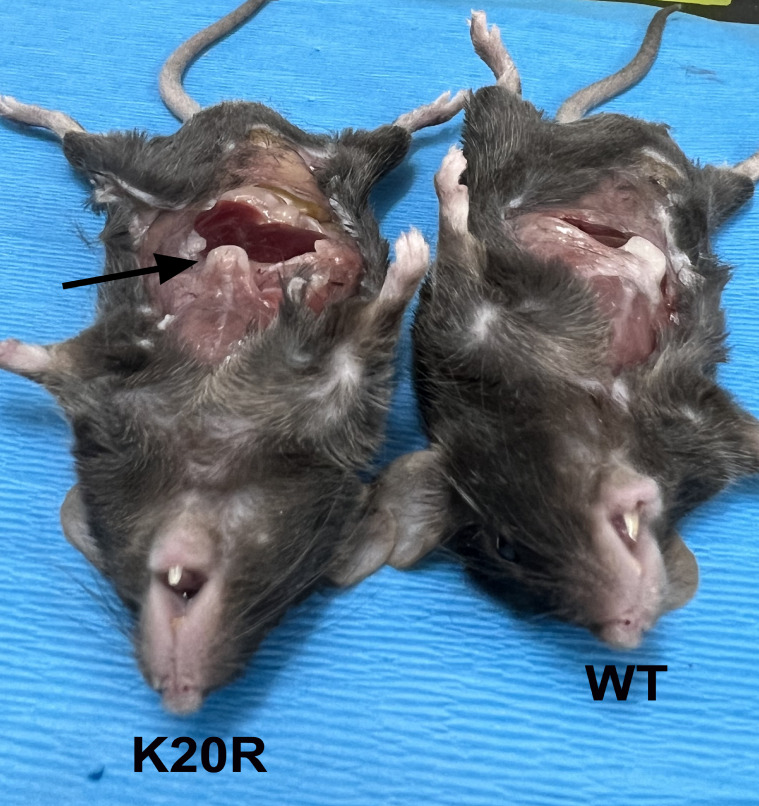
Figure 7. K20R mutation causes hepatosplenomegaly and expansion of hematopoietic populations.
(A and B) The enlarged liver or spleen from the homozygous K20r mutant mice, as compared to that of the Ezh2 wild-type mice (8 months old). The weights of livers or spleens from the K20r and wild-type Ezh2 mice (7~10-month-old) were measured and plotted. Values are means ± SEM (N=6, *P<0.05). (C) Number of total cells in bone marrows harvested from 5-month-old K20r and wild-type Ezh2 mice. Values are means ± SEM (n=9, ****p<0.0001). (D–F) Representative flow cytometric (FACS) profiles of bone marrow cells from the K20r and Ezh2 wild-type mice. Flow cytometry plots were gated on the Lin-cKit+ (myeloid progenitors) subpopulation that is subclassified into common myeloid progenitor (CMP), granulocyte-monocyte progenitor (GMP), and myeloid erythroid progenitor (MEP) based on Lin-cKit+ CD16/32 and CD34 expression. The number of immature cells Lin-cKit+Scal1+(E), Lin-cKit+ (F), CMP, GMP, and MEP in (G), and differentiated cells Mac1+Gr1+ myeloid (H) and Ly6.6G myeloid (I) in bone marrow samples harvested from the Ezh2 wild-type and K20r mutant mice. Values are means ± SEM (n=6–9). Significance was indicated as a two-tailed, unpaired, t-test. *p<0.05.***p<0.001. ****p<0.0001. (J) The quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis shows mRNA expression levels of indicated genes in bone marrow samples harvested from the Ezh2 wild-type and K20r mutant mice.