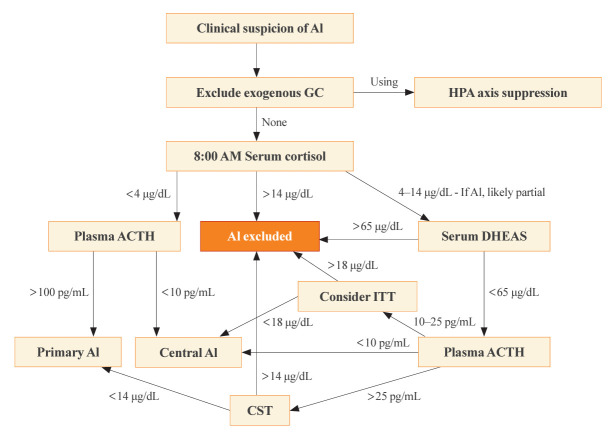
Fig. 1.
Diagnostic algorithm for evaluating adrenal function. After excluding exogenous glucocorticoid use, the 8:00 AM serum cortisol is the first step. If the cortisol is conclusively low (<4 µg/dL), then plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) determines if it is primary or central adrenal insufficiency (AI). If the cortisol is 4 to 14 µg/dL, the patient might have AI, but it is likely partial, and the lower the 8:00 AM cortisol the more likely that some degree of AI is present. In these cases, a dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEAS) >65 µg/dL excludes AI; if not, ACTH determines if dynamic testing with cosyntropin stimulation test (CST) or insulin tolerance test (ITT) is recommended to determine if primary or central AI is present. Clinical judgment should always take precedence over laboratory test results when making a diagnosis of AI and subjecting patients to chronic glucocorticoid therapy. GC, glucocorticoids; HPA, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal.