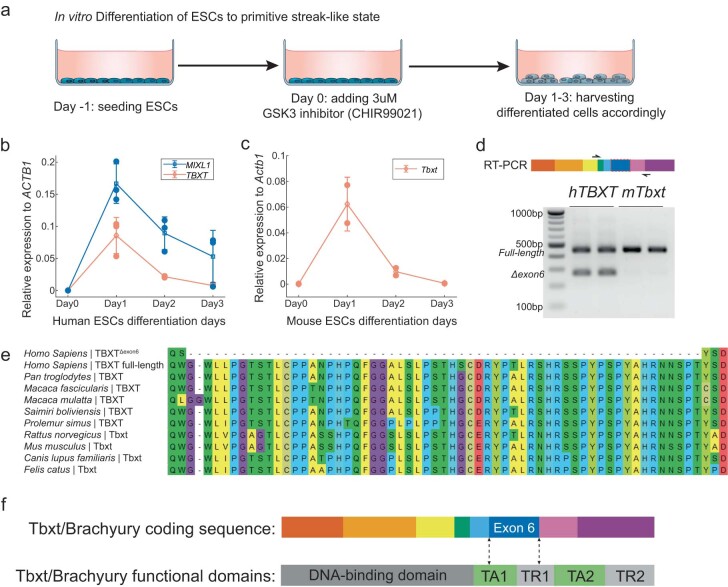
Extended Data Fig. 3. Analyses of TBXT isoforms.
a, In vitro differentiation of human and mouse ESCs for inducing TBXT/Tbxt expression. Human and mouse ESCs differentiation assay was adapted from Xi et al. (2017)36 and Pour et al. (2019)37, respectively. Schematic adapted from icons created by Marcel Tisch via bioicons.com. b, Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) of TBXT and MIXL1 expression during hESC differentiation, indicating correct induction of mesodermal gene expression program36. c, Quantitative RT-PCR of Tbxt expression during mESC differentiation. Data in b and c were presented as mean +/− standard deviation of the relative gene expression levels. Sample number n = 3 represents RT-qPCR results from three biologically independent RNA samples, with each data point averaged from 3 technical replicates in quantitative PCR. d, RT-PCR of TBXT/Tbxt transcripts in human and mouse differentiated ESCs, highlighting the Δexon6 splicing isoform unique to human. RT-PCR results were presented as biological duplicates. e, Protein sequence alignment of TBXT-exon6 region in the representative mammals. All presented animals have tails except human and chimpanzee. f, The exon 6-coded peptide of Tbxt protein overlaps with large fractions of two transcription regulation domains. TA, transcription activation; TR, transcription repression. Functional domain annotation of mouse Tbxt protein was adapted from Kispert et al. (1995)9.