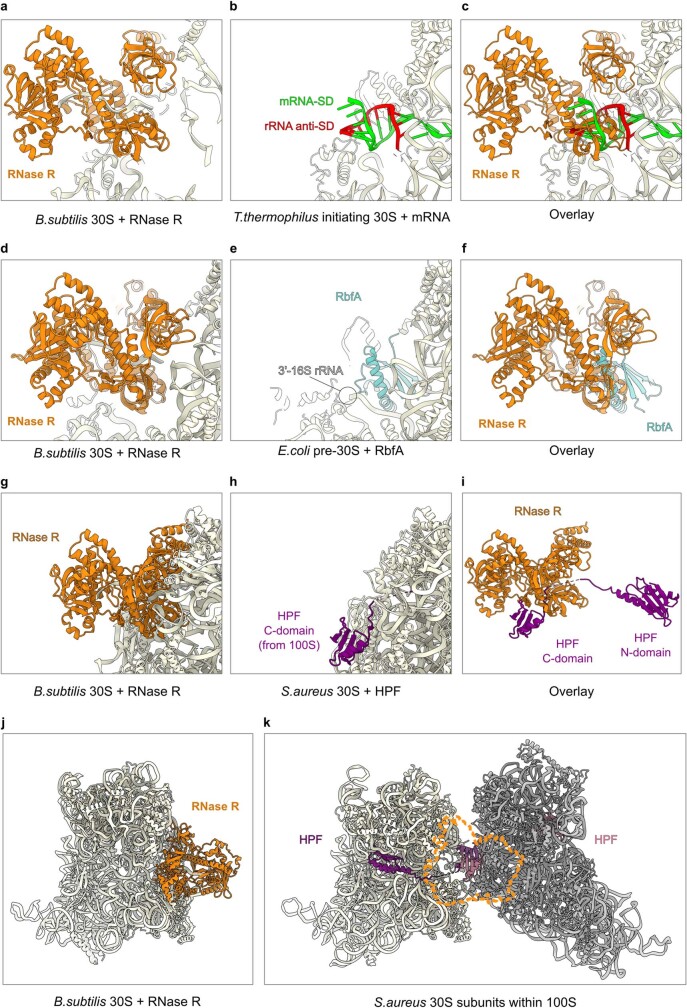
Extended Data Fig. 8. Comparison of the binding site of RNase R in the state I RNase R–30S complex with factors and ligands.
a–c, The binding site of RNase R (orange) in state I RNase R–30S complex (a), Shine–Dalgarno-anti-SD with mRNA (green) and 3′ end of 16S rRNA (red) bound to the Thermus thermophilus 70S ribosome (PDB ID 5LMN)48 (b) and overlay of RNase R (orange) and SD–anti-SD helix (green-red) (c) from a,b. d–f, The binding site of RNase R (orange) in state I RNase R–30S complex (d), RbfA (cyan) bound to the E. coli pre-30S complex (PDB ID 7BOH)50 (e) and overlay of RNase R (orange) and RbfA (cyan) (f) from d,e. g–i, The binding site of RNase R (orange) in state I RNase R–30S complex (g), HPF (purple) bound to the S. aureus 30S within the 100S disome (PDB ID 6FXC)53 (h) and overlay of RNase R (orange) and HPF (purple) (i) from g,h. j,k, The binding site of RNase R (orange) in state I RNase R–30S complex (j), compared with dimerized HPF (purple) and 30S subunits from the S. aureus 100S (PDB ID 6FXC)53 (k).