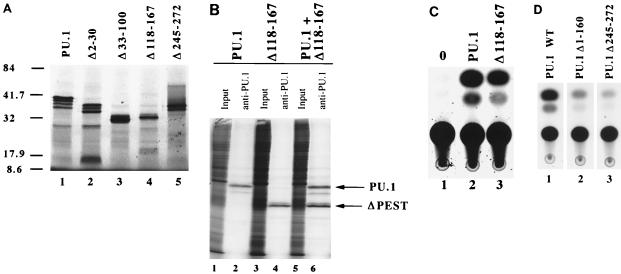
FIG. 1.
Stable expression of and transactivation by PU.1 mutant proteins. (A) SDS-PAGE of in vitro-transcribed and -translated PU.1 mutant proteins. All constructs produced proteins of the predicted molecular sizes (indicated in kilodaltons) based on the engineered mutation. (B) Immunoprecipitation of metabolically labeled PU.1 and Δ118-167 proteins. Lanes 1, 3, and 5, total labeled protein prior to immunoprecipitation; lanes 2, 4, and 6, anti-PU.1 antibody-precipitated proteins of the predicted molecular weights for the engineered mutation. All PU.1 variants were equivalently expressed and stable in NIH 3T3 cells. (C) CAT transactivation assays of PU.1 and Δ118-167, using a multimerized PU.1 binding site from the immunoglobulin kappa 3′ enhancer region (34). Lane 1, cells containing the reporter construct and no PU.1 protein; lane 2, activation by the wild-type PU.1 protein; lane 3, activation by Δ118-167 mutant protein. (D) CAT transactivation of the same kappa 3′ enhancer element, using wild-type (WT) and mutant PU.1 proteins with Pip, c-Fos, and c-Jun as described elsewhere (35).