Figure 6.
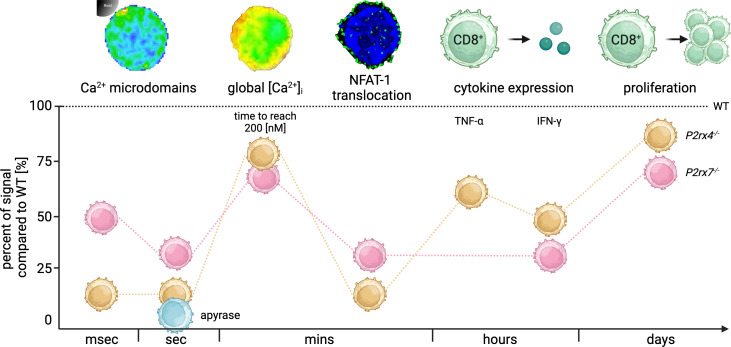
Summary of the time-resolved role of P2X4 and P2X7 during CD8+ T cell activation. Summary of the significant signal reduction in CD8+ T cells from P2rx4-/- and P2rx7-/- compared to the WT (dashed line) in milliseconds (msec), seconds (sec), minutes (mins), hours and days after TCR stimulation. In the first msec Ca2+ microdomains were reduced in P2rx4-/- and P2rx7-/- T cells by 85% and 54%. Seconds after stimulation the Ca2+ microdomains were reduced by 91% and 78%. Moreover, the hydrolysis of eATP by the addition of apyrase (blue) reduces the number of Ca2+ microdomains by 99% in the first 15 seconds in WT CD8+ T cells. The global Ca2+ response in the first mins after stimulation was delayed and the cells lacking either P2X4 or P2X7 showed only 16% or 19% of the time to reach 200 nM Ca2+ compared to the WT. The translocation of the nuclear factor NFAT-1 was decreased in P2rx4-/- and P2rx7-/- T cells by 71% and 81% after mins, whereas cytokine expression of IFN-γ was decreased by 52% and 67%. Only in CD8+ T cells from P2rx4 -/- mice, the number of TNF-α expressing cells was significantly reduced by 33%. Furthermore, the proliferation of the cells was affected by a reduction of 15% and 25% compared to WT cells. (Created with BioRender.com).