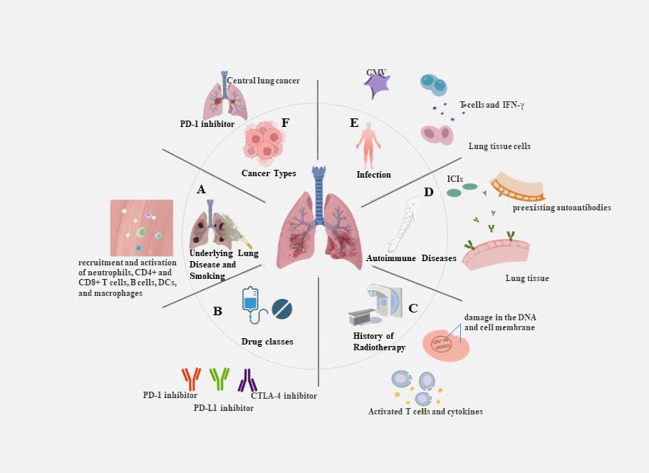
Figure 2.
Risk factors for the occurrence of CIP. (A) Underlying lung disease and smoking: e.g. The inflammatory microenvironment in COPD patients is accompanied by the recruitment and activation of neutrophils, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. (B) Drug classes: e.g. PD-1 inhibitors revealed an increase in the incidence of pneumonia of any grade in comparison with PD-L1 inhibitors. (C) History of radiotherapy: e.g. The combination of DNA damage caused by radiotherapy and the reactivation of T cells by immunotherapy results in the release of large amounts of cytokines. (D) Autoimmune diseases:e.g. Patients treated with ICIs modulates humoral immunity and enhances preexisting autoantibodies. (E) Infection: e.g. CMV infection or reactivation can lead to severe disease in the absence of an effective immune response, with increased CD8+ T cell sensitivity and elevated levels of circulating IFN-γ. (F) Cancer types: e.g. Squamous cell carcinomas are predominantly central lung cancers that are more prone to causing obstructive pneumonia.