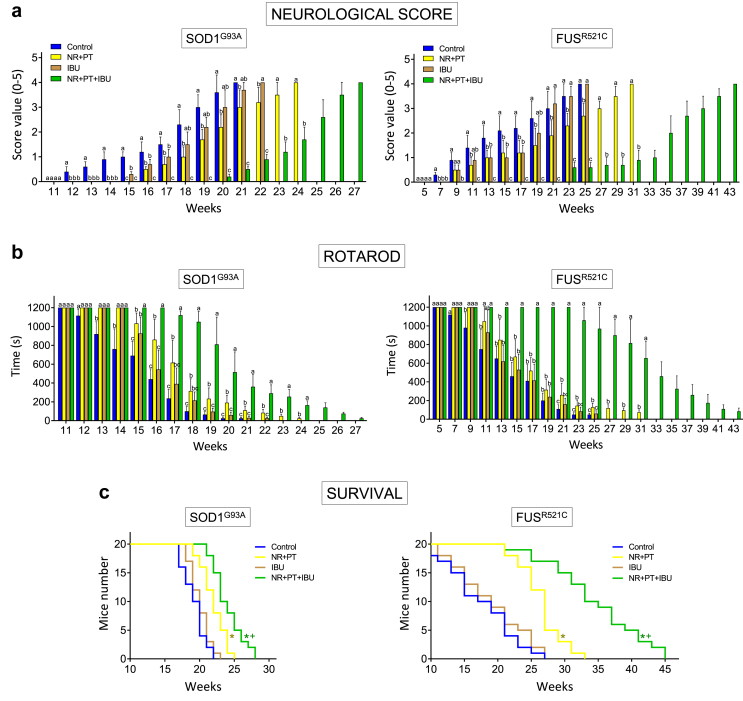
Fig. 1.
NR + PT + IBU delay loss of functional performance and extend survival in SOD1G93A and FUSR521C mice. (a) Neurological score. (b) Rotarod test. (c) Survival. Treatment arms were as follows: physiological saline-treated transgenic mice (controls), SOD1 G93A or FUSR521C mice treated with NR and PT, SOD1 G93A or FUSR521C mice treated with IBU, and SOD1 G93A or FUSR521C mice treated with NR, PT and IBU. The number of mice tested per week (tests a and b) was identical to that displayed in the survival experiments (c) for each experimental group. Both neuromotor tests (a, b) were performed twice a week. On the days of the week in which the animals were not scored, they were trained in the rotarod. Control experiments performed in WT mice (n = 10) rendered a neurological score of 0 and a performance time of 1200 s in the rotarod test in all cases. Taking into account the % of animals that died during disease progression, to assess the neurological score and the rotarod test, their number was increased so that n (15 mice) was approx. the same both at onset and at advanced progression. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to make comparisons among the different treatments at each time point. Different letters indicate statistical differences, P < 0.05 (a, b). Survival data were analyzed with Kaplan-Meier curves and LogRank (Mantel-Cox) test (∗P < 0.01 comparing all groups versus controls; +P < 0.01 comparing mice treated with NR + PT + IBU versus mice treated with NR + PT) (c).