Fig. 3.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
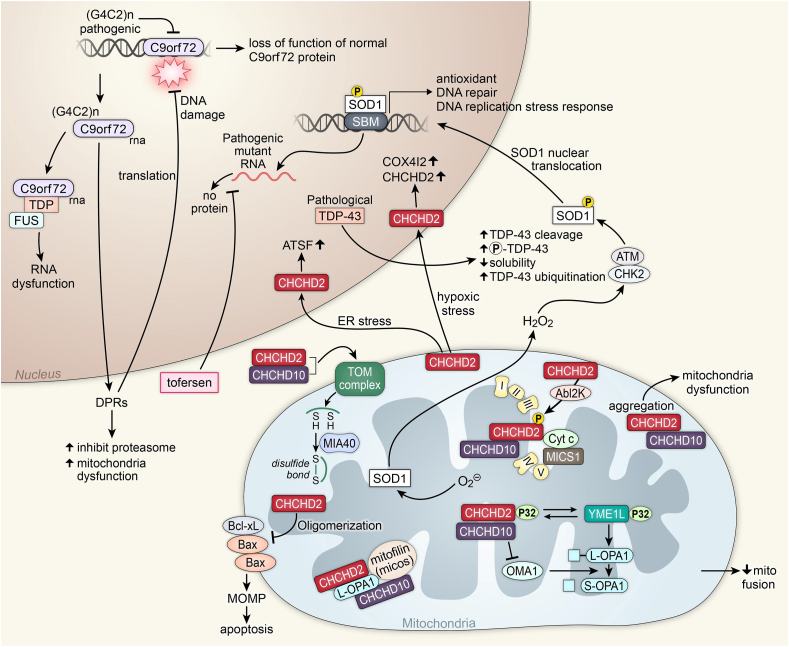
Above is a figure illustrating mitochondrial affecting pathways in ALS associated with CHCHD2, CHCHD10, C9orf72, TDP-43, and SOD1. Superoxide activates the SOD1 protein. SOD1, with hydrogen peroxide and a CHK2 ATM complex, is phosphorylated, which allows it to enter the nucleus through SOD1 nuclear translocation. In the nucleus, it functions as a transcription factor on SBM to transcript antioxidants proteins, DNA repair proteins, and proteins for the DNA replication stress response. Pathogenic SOD1 creating mutant RNA will produce no protein. Tofersen inhibits this process. Pathological TDP-43 leads to increased TDP-43 cleavage, increased phosphorylation of TDP-43, decreased solubility, and increased TDP-43 ubiquitination. Pathogenic (G4C2)n inhibits the expression of normal C9orf72, leading to the loss of function of normal C9orf72 protein. (G4C2)n C9orf72 RNA is transcribed, leading to DPRs that inhibit the proteasome and lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. DPRs also lead to DNA damage. The (G4C2)n C9orf72 RNA can also create a complex with TDP and FUS, leading to RNA dysfunction. With hypoxic stress, CHCHD2 will enter the nucleus and increase COX4I2 and CHCHD2. Under ER stress, CHCHD2 will enter the nucleus and increase ATSF. CHCHD2 works with AbI2k to phosphorylate a CHCHD2, CHCHD10, Cyt c, and MICS1 complex in the ETC. Oligomerization of CHCHD2 leads to inhibition of the Bcl-xL, Bax, and Bax complex, leading to MOMP and apoptosis. Aggregates of CHCHD2 and CHCHd10 in the mitochondria lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. A CHCHD2 and CHCHD10 complex activate a TOM complex, creating disulfide bonds with MIA40. A complex of CHCHD2, CHCHD10, and p32 transfers the p32 to YME1L. The YME1L p32 complex cleaves L-OPA1 to become S-OPA1 with OMA1. OMA1 is inhibited by the CHCHD2, CHCHD10, and p32 complex, decreasing mitochondrial fusion.