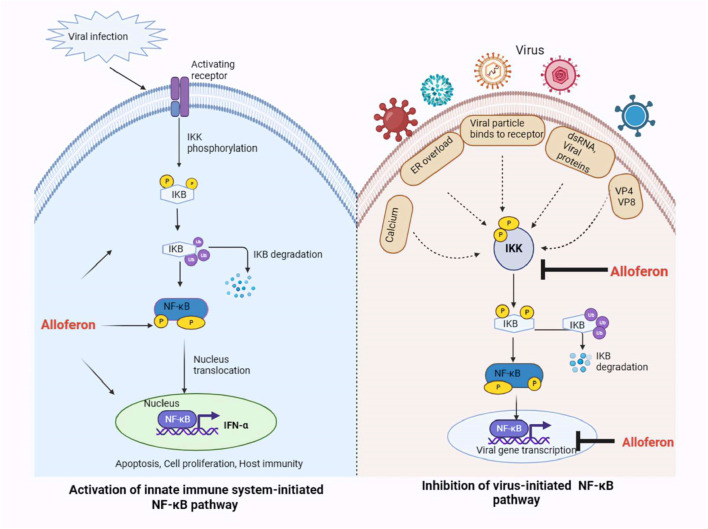
FIGURE 2.
Hypothetical model for the antiviral effect of alloferon via the NF-κB pathway. Alloferon may act as an activator or inhibitor of the NF-B pathway depending on the function of the pathway in the host. During viral infections, alloferon treatment may help activate receptors and signals that boost the NF-κB pathway through IKK phosphorylation. Activation of NF-κB by alloferon causes stimulation of the IFN-α which is responsible for boosting the innate immune system to fight against the cancer or virally infected cells. On the other hand, some viruses may alter the NF-κB pathway for their benefit to induce stress responses and prevent apoptosis of the infected cells. Alloferon treatment may then act as an inhibitor of the NF-κB pathway by preventing IKK activation and blocking expression of the viral gene because some viruses possess binding sites for transcription by NF-κB.