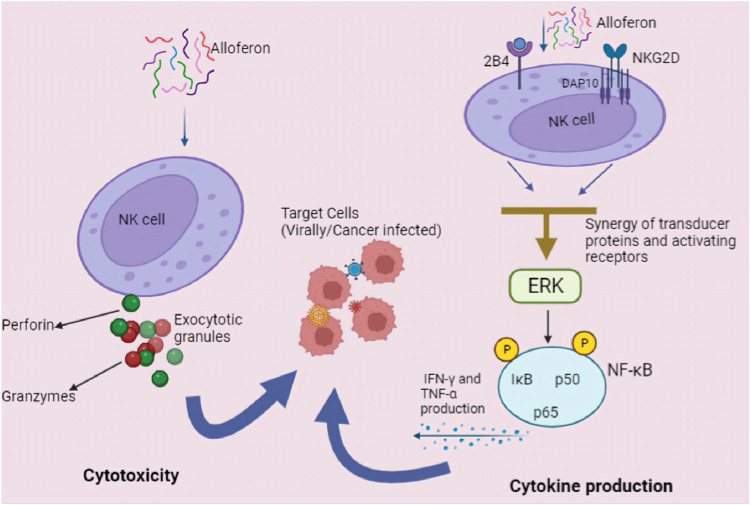
FIGURE 3.
Anticancer and antiviral mechanisms of alloferon. NK cells provide early protection against cancerous and viral infected cells by producing cytokines and exerting direct cytolytic activity. Alloferon increases NK cells’ cytotoxicity following two main mechanisms: (1) Cytotoxicity via secretion of lytic/exocytotic granule. The lytic granules: perforin and granzymes functions after infected cell and NK cell interaction. Perforin causes the cell to become permeable whereas granzymes cause damage to DNA, stop the cell cycle, and destroy the nucleus when they enter the cell. (2) Increasing the production of IFN-γ and TNF-α via the NF-κB pathway. Through the generation of IFN-γ, activated NK cells generate effector activity that directly reduces host cell hospitability to the virus and can operate indirectly to prevent infection in other cells. Additionally, they recruit and activate additional effector leukocytes.