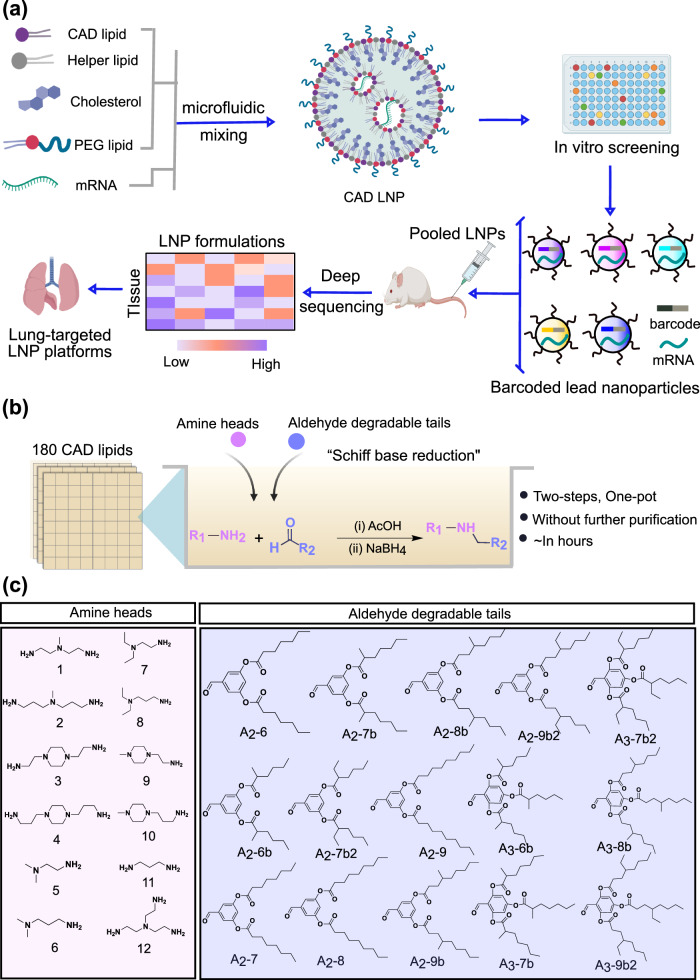
Fig. 1. High-throughput LNP screening facilitates the discovery of cationic degradable (CAD) lipid-like materials for mRNA delivery to the lungs.
a CAD LNPs were initially formulated using a microfluidic mixing device by mixing nucleic acid with CAD lipids, helper lipid, cholesterol, and PEG-lipid. Following in vitro high-throughput screening, a series of CAD LNPs were selected and formulated to co-encapsulate b-DNA and mRNA, pooled, and systemically administered into mice, allowing for quantification of accumulation in each organ (heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys) using deep sequencing to identify CAD lipid candidates for lung-targeted mRNA delivery. b A combinatorial library of CAD lipids was chemically synthesized through “Schiff base reduction” by reacting amine heads and aldehyde degradable tails. c Overview of 12 amines cores and 15 aldehyde degradable tails used to synthesize 180 CAD lipids. a Created with BioRender.com.