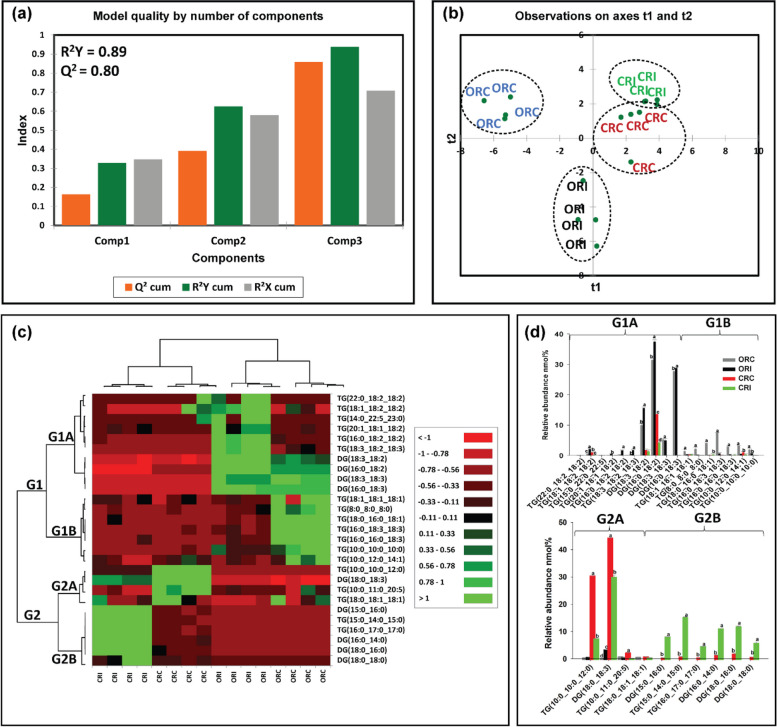
Fig. 8.
Differences in root glycerolipid species in susceptible (OX760-6) and tolerant (Conrad) soybean cultivars inoculated with P. sojae relative to control plants. a Model quality for partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA); (b) Observation plot based upon differences in molecular species in root glycerolipid species of OX760-6 and Conrad cultivars; (c) Heat map demonstrating clusters of root glycerolipid species in OX760-6 and Conrad cultivars treated or untreated with P. sojae. Each cultivar and treatment were grouped separately using ascendant hierarchical cluster analysis based upon Euclidian distance at interquartile range of 0.15. The left columns denote the cluster segregated root glycerolipid species, while the above columns segregated soybean cultivars based upon similarities in abundance. The abundance of root glycerolipid species is denoted using color: red for lower level, black for intermediate level, and green for higher level. Group 1 and 2 (G1 and G2) and subgroups (G1A, G1B, G2A and G2B) are root glycerolipid species that were accountable for the formation of clustered patterns in the heat map that were applied for determination of significant differences between the soybean cultivars (OX760-6 and Conrad) root glycerolipid species in each of the bar chart (Fig. 7d) beside the heat map; and (d) Bar charts describe the relative abundance of root glycerolipid species as a mean nmol% ± SE (n = 4). Significant differences between root glycerolipid species are indicate using letter a-d on top of the bars as described by Fisher's LSD multiple comparisons test using ANOVA (α = 0.05). The G1 and G2, and G1A, G1B, G2A and G2B are root glycerolipid species that were accountable for the formation of clustered patterns in the heat map that were applied for the determination of significant differences between the soybean cultivars (OX760-6 and Conrad) root glycerolipid species as illustrated in the bar charts. The susceptible cultivar, ORC (non-infected) & ORI (infected), and the tolerant cultivar CRC (non-infected) & CRI (infected)