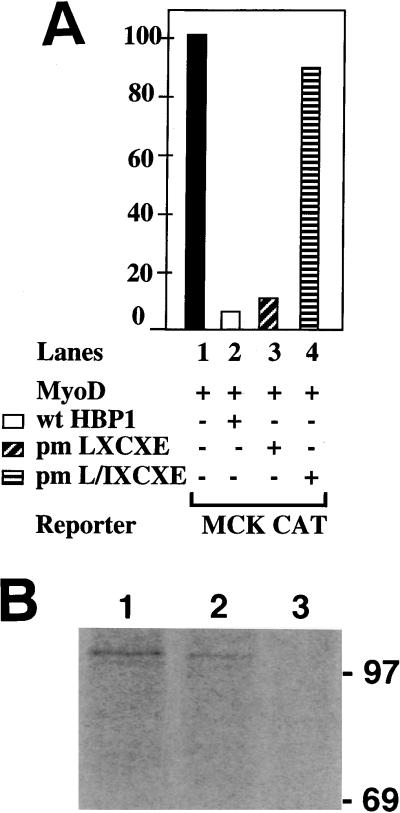
FIG. 9.
Regulation of MyoD family transcriptional activation by HBP1 and RB. (A) Effect of HBP1 mutants on MyoD activation of a MCK-CAT reporter construct. The role of RB binding in the inhibition of MyoD family activation was tested by using the indicated mutants of HBP1. As described in Fig. 1 and reference 49, the wild-type HBP1 and pm-LXCXE are functional in RB binding and in repression of the N-MYC promoter, but the pm-L/IXCXE is defective in both functions. The indicated proteins were expressed in conjunction with MyoD: lane 1, no HBP expression vector (filled bar); lane 2, wild-type HBP1 (open bar); lane 3, pm-LXCXE (diagonal stripes); and lane 4, pm-L/I XCXE (horizontal stripes). (B) In vivo association of RB and HBP1 in differentiated C2C12 myotubes. HBP1 was shown to interact with RB in differentiated C2C12 myotubes. C2C12 were completely differentiated for 4 days in DMEM supplemented with 2% FCS. Cells were metabolically labeled with 35S-methionine, and cell lysates were collected for double immunoprecipitations as described in Materials and Methods. The first immunoprecipitations were carried out with anti-RB antibodies (lane 1) or anti-HBP1 antibodies (lanes 2 and 3), and the second immunoprecipitations were carried out with anti-RB antibodies (lanes 1 and 2) and anti-β-Gal antibodies (lane 3). Note that the amount of extracts used in lane 1 was approximately one-sixth of that used in lane 2 or 3.