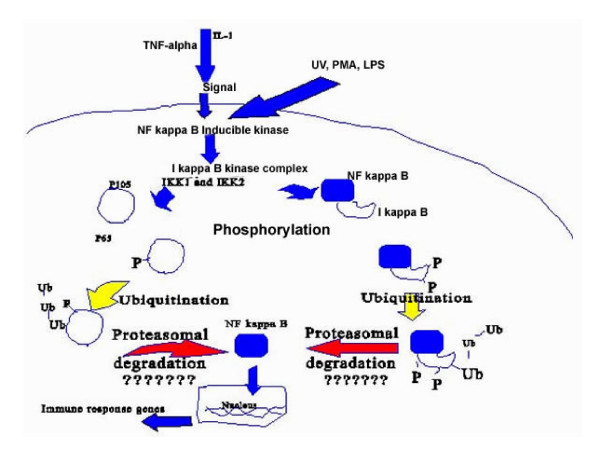
Figure 4.
The steps involved in the activation of NF-κB family of transcription factors (Reproduced from Ponnappan, 1998, Feb 01; 3:d152-68 with permission from Frontiers in Bioscience). Activators of NF-κB like TNF-alpha, PMA, UV or LPS activate the NF-κB inducible kinase, which in turn phosphorylates at least IKK1 (I kappa B kinase-alpha) and sometimes IKK2 (I kappa B kinase-beta) in the I kappa B-kinase complex. Activators of NF-κB may directly activate the kinase complex as well. This may be followed by phosphorylation of the p105/p65 complex by the kinase complex, which is in turn followed by ubiquitination, proteasomal degradation and the nuclear translocation of NF kappa B. Inside the nucleus; NF kappa B promotes the transcription of immune response genes. The "??????" indicates the possibility of lowered translocation and consequent activation of NF-κB, which occurs in various diseases.