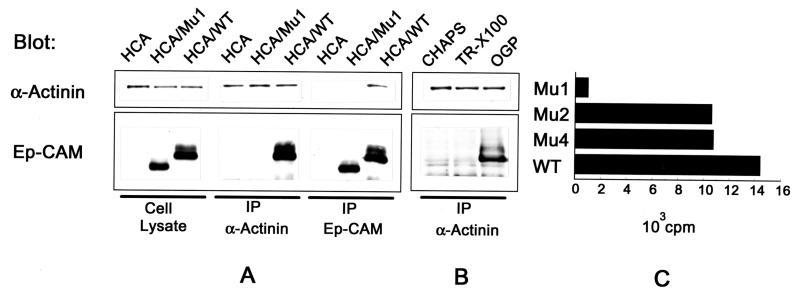
FIG. 9.
Interaction of Ep-CAM and α-actinin. (A) Detection of Ep-CAM and α-actinin by immunoblotting with the respective antibodies (323/A3 and CB-11) in cell lysates and immunoprecipitates (IP) obtained with antibodies to Ep-CAM (MAb 323/A3) and α-actinin (polyclonal serum) from 50 mM n-octylglucoside extracts of the parental HCA cells, Mu1, or wild-type (WT) Ep-CAM transfectants. (B) Detection of Ep-CAM and α-actinin in immunoprecipitates with anti-α-actinin antibody from lysates of HCA/WT transfectants prepared with either CHAPS (50 mM), Triton X-100 (0.2%), or n-octylglucoside (OGP [50 mM]). Note that Ep-CAM is coprecipitated only from the lysates obtained with n-octylglucoside. (C) Binding of α-actinin to a solid-phase immobilized wild-type and mutant Ep-CAM molecules. Mu1, -2, and -4 and wild-type Ep-CAM from 1% Triton X-100 (TR-X100) lysates of the respective HCA cell transfectants were immobilized on Sac-Cel beads precoated with anti-Ep-CAM MAb. Binding of 125I-α-actinin to the immobilized wild-type or mutant Ep-CAM molecules is presented after subtraction of the background binding of α-actinin to the beads precoated with nontransfected HCA cell lysate.