Figure 1.
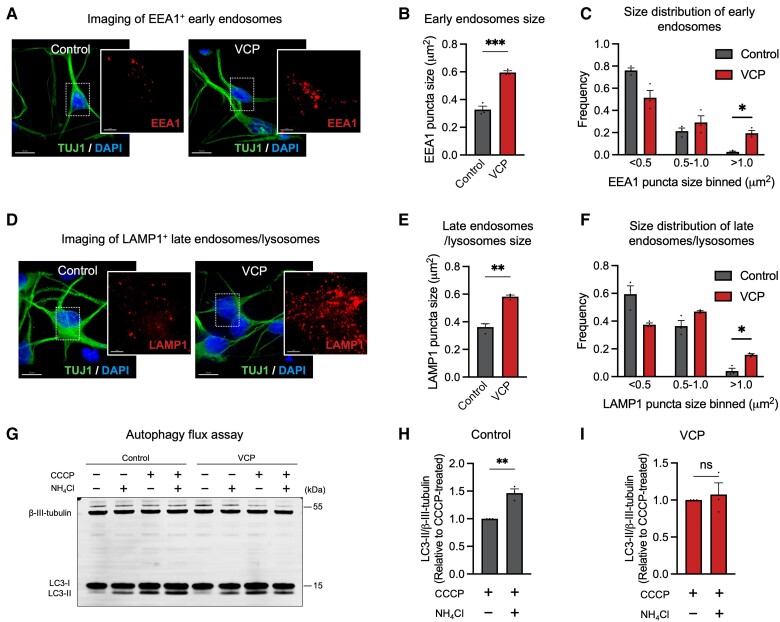
Abnormal accumulation of enlarged endosomes and lysosomes in VCP mutant cortical neurons. (A–C) Representative immunocytochemistry of human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived neurons expressing EEA1 proteins (A) (red = EEA1; green = TUJ1; blue = DAPI). Scale bars = 10 μm. A significant increase in the average size of EEA1+ puncta (B) and frequency (C) of early endosomes with size > 1 μm2 in VCP mutant neurons (n = 3 control and n = 3 VCP mutant lines). (D–F) Representative immunocytochemistry of hiPSC-derived neurons expressing LAMP1 proteins (D) (red = LAMP1; green = TUJ1; blue = DAPI). Scale bars = 10 μm. A significant increase in the average size of LAMP1+ puncta (E) and frequency (F) of late endosomes/lysosomes with size > 1 μm2 in VCP mutant neurons (n = 3 control and n = 3 VCP mutant lines). (G) Autophagic degradation was calculated by comparing LC3-II levels following treatment with autophagy activators (CCCP) in the presence or absence of NH4Cl. Representative western blots of LC3I/II and neuron-specific β3-tubulin are shown (G). (H and I) Autophagosome degradation was significantly impaired in VCP mutant neurons, as calculated from the western blot analysis. A further elevation of LC3-II levels was only observed in control neurons (H) but not in VCP mutant neurons (I) (one-sample t-test) (n = 3 control and n = 3 VCP mutant lines).