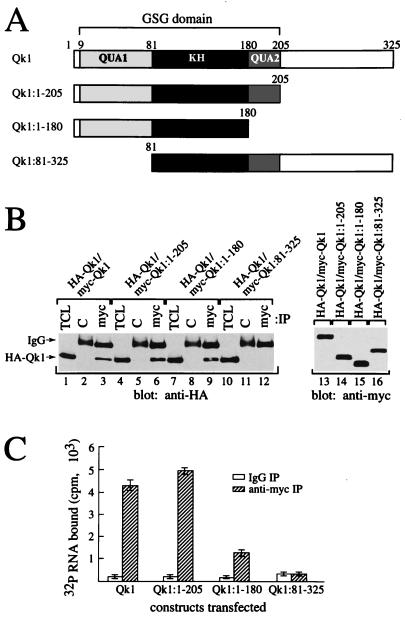
FIG. 3.
Mapping of the Qk1 self-association and RNA binding regions within the GSG domain. (A) Schematic diagrams of the Qk1 constructs utilized are shown. The black box denotes the KH domain, whereas the gray boxes represent the QUA1 and QUA2 regions as indicated. The entire region encompassing QUA1, KH, and QUA2 is the GSG domain. (B) Truncation of the N-terminal 80 amino acids of Qk1 or QUA1 abolishes self-association. HA-Qk1 was cotransfected in HeLa cells with various myc-Qk1 deletion constructs as indicated. Total cell lysates (TCL) as well as anti-myc (myc) and control IgG (C) immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibodies. Total cell lysates of the myc-Qk1 proteins were immunoblotted with anti-myc antibodies (lanes 13 to 16). (C) The Qk1 GSG domain is required for RNA binding. HeLa cell lysates containing myc-tagged Qk1 or various truncated forms of Qk1 were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody (hatched bars) or control IgG (white bars) and then incubated with 32P-labeled total cellular RNA. Each bar represents the mean ± standard deviation of data from more than six independent immunoprecipitations carried out during more than three separate experiments.