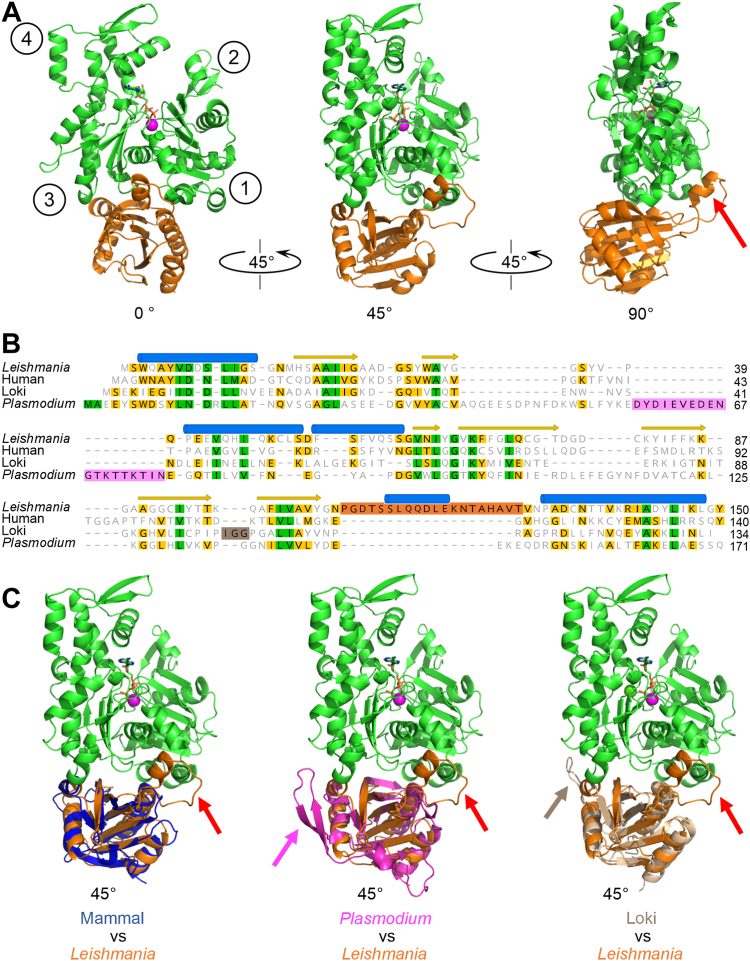
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of Leishmania major profilin (LmProfilin) in complex with actin.A, three orientations (0o, 45o, and 90o) of the co-crystal structure of LmProfilin (orange)–actin (green) complex. The ATP nucleotide (brown) and the associated Ca2+ ion (magenta ball shaped) in actin are highlighted. The subdomains of actin are labeled by one to four numbers in circles. The specific insertion in Leishmania profilin is indicated with a red arrow in the panel on the right. B, structure-based protein sequence alignment (performed by Dali server (72)), of profilins from trypanosomatid parasite (L. major, Protein Data Bank [PDB] ID: 8C47, chain B; UniProt: Q4Q5N1), human (Homo sapiens, PDB ID: 6NBW, chain C; UniProt: P07737; (73)), Asgard archaea (Lokiarchaeum, PDB ID: 5ZZB, chain B; UniProt: A0A0F8V8L2; (36)), and malarial parasite (Plasmodium falciparum, PDB ID: 2JKG, chain A; UniProt: Q8I2J4; (37)). Specific insertions, which are not present in mammalian profilin, are highlighted by pink in Plasmodium, by orange in Leishmania, and by light brown in Loki profilin sequences. C, superimposition of the profilins from human, Plasmodium, and Asgard archaea with the Leishmania profilin, when in complex with an actin monomer. The positions of Leishmania, malaria parasite, and Lokiarchea-specific insertions in the structures are indicated with red, pink, and light brown arrows, respectively. A view of 45o was selected to better visualize the locations of the insertions in all three profilins.