Fig. 1.
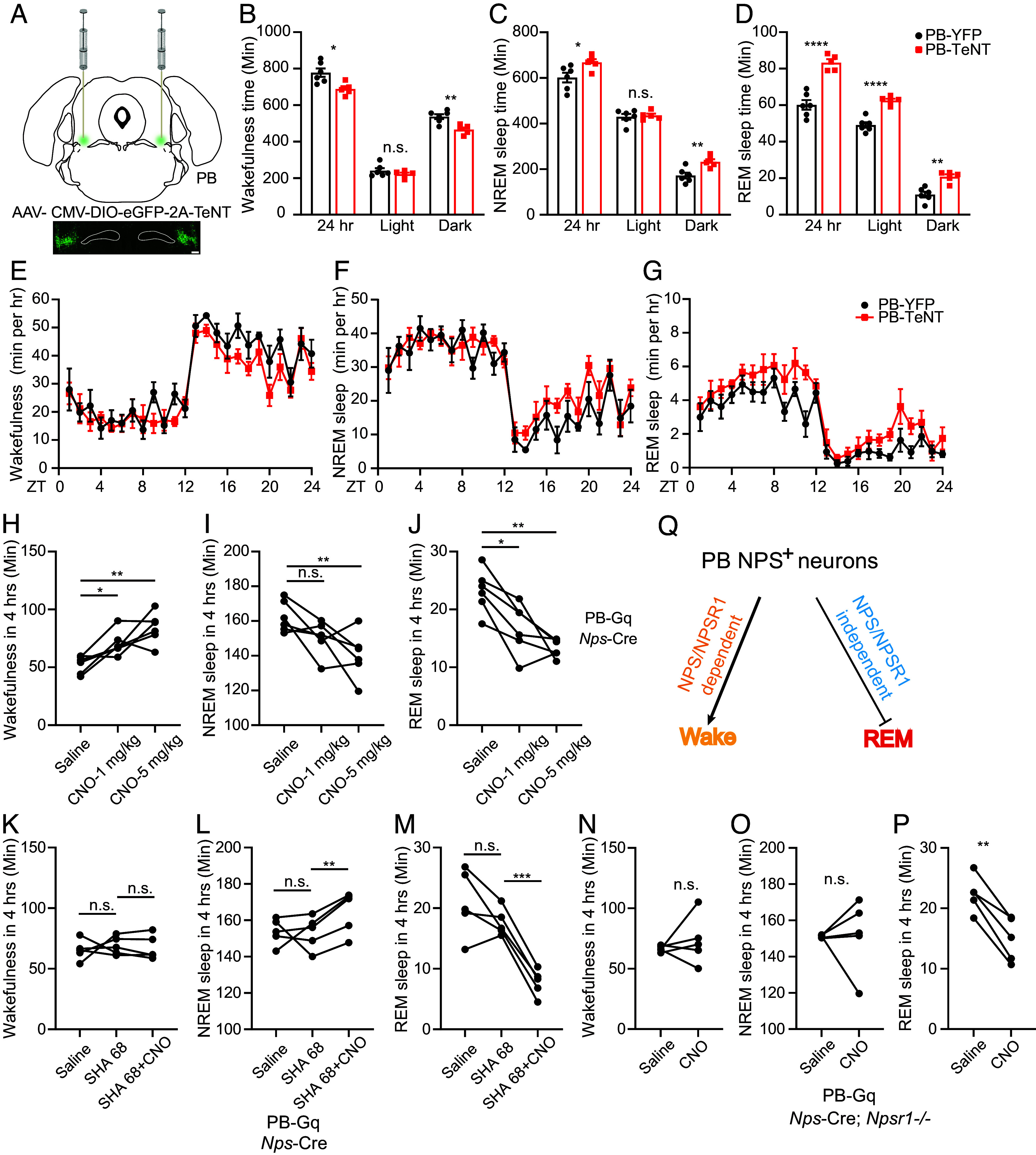
PB NPS+ neurons are wake-promoting. (A) Schematic of TeNT inhibition of PB NPS+ neurons. (B–D) Total wakefulness time (B), NREM sleep time (C), and REM sleep time (D) by EEG/EMG within 24 h, light phase, and dark phase were calculated in YFP (n = 6) and TeNT (n = 5) injected mice. (E–G) Total wakefulness (E), NREM sleep (F), and REM sleep (G) were plotted hourly for 24 h in YFP (n = 6) and TeNT (n = 5) injected mice. (H–J) Quantified results for total wakefulness (H), NREM (I), and REM (J) sleep recorded 4 h after saline or CNO injection at ZT6 in the hM3Dq (n = 6) injected mice. (K–M) Quantified results for total wakefulness (K), NREM (L), and REM (M) sleep recorded 4 h after saline (Left column), SHA 68 (Middle column) or SHA 68+CNO (5 mg/kg) (Right column) injection at ZT6 in the hM3Dq (n = 5) injected mice. (N–P) Quantified results for total wakefulness (N), NREM (O), and REM (P) sleep recorded 4 h after saline or CNO (5 mg/kg) injection at ZT6 in the hM3Dq (n = 5) injected Nps-Cre; Npsr1−/− mice. (Q) Schematic showing effect of NPS/NPSR1 signaling in the sleep/wake regulation activity of PB NPS+ neurons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, n.s. = not significant. Two-tailed Student’s t test for (B–D) and (H–P). Two-way ANOVA, post hoc Sidak’s multiple comparisons test for (E–G). RM one-way ANOVA, post hoc Dunnett's multiple comparisons test for (H–M). Error bars represent ± SEM. (Scale bar, 200 μm.)
