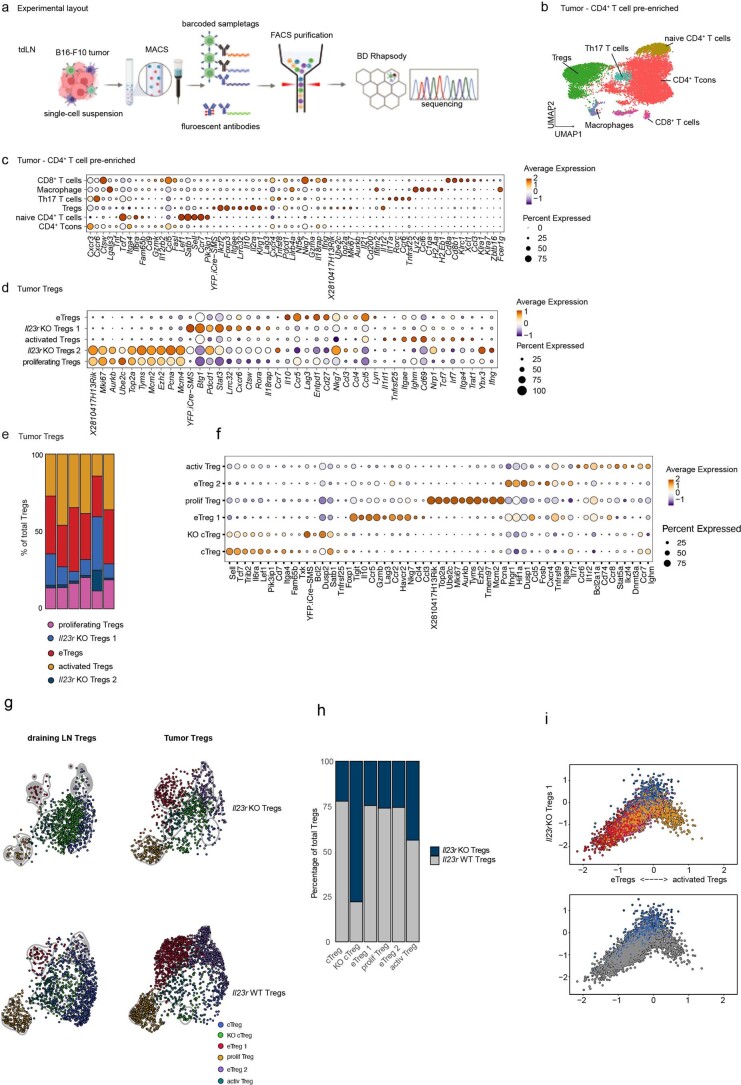
Extended Data Fig. 5. IL-23 sensing by Treg cells initiates an eTreg cell program in the murine TME.
(a-i) Foxp3Cre-YFP/+ (heterozygous) Il23rfl/fl female mice were inoculated i.d. with B16 tumor cells and combined transcriptome (scRNAseq) and protein expression analysis of sorted CD4+T cells was performed on day 13 post-inoculation. Data shown from one experiment with n = 6. (a) Schematic illustration of the experimental workflow. (b) UMAP displaying clustered (based on transcriptome expression) and manually annotated cell subsets passing quality control. (c) Dotplot depicting the 10 most variable features in all identified cell subsets. (d) Dotplot displaying the 10 most variable features across identified Treg cell subsets. (e) Bar chart displaying the frequencies of Treg cell subsets of total tumor Treg cells. (f) Dotplot of the most variable features of Treg cell subsets of integrated tumor and tumor-draining lymph node Treg cells. (g) UMAPs highlighting the distribution of Il23r KO and WT Treg cells across identified clusters in tumors and tumor-draining lymph nodes. (h) Bar chart of percentages of Il23r KO and WT Treg cells across Treg cell clusters. (i) Cellular state plot displaying enrichment of module scores of identified Treg cell subsets compared to gene modules of activated vs. eTreg cells (x-axis) and KO Treg cells (y-axis).