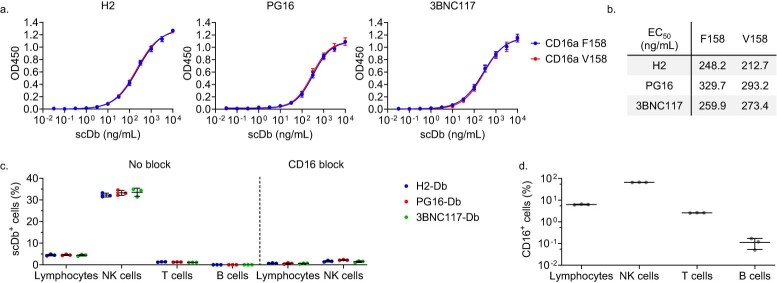
Extended Data Fig. 1. H2-Db, PG16-Db, and 3BNC117-Db bind both CD16a recombinant protein and cell surface CD16a.
a, Binding of H2-Db, PG16-Db, 3BNC117-Db to immobilized CD16a recombinant proteins. Both CD16 variants are identical except for a single amino acid substitution at position 158 (F/V). Data reported as the optical density at 450nm (OD450) (mean, SD) from three replicates and were fitted to a dose-response nonlinear regression model. b, Calculated EC50 values for the fitted nonlinear regression model from a reported in ng/mL. c, Binding of H2-Db, PG16-Db, and 3BNC117-Db to peripheral blood lymphocytes, CD3−CD56+ NK cells, CD3+ T cells, and CD19+ B cells with or without blocking with a CD16-specific antibody (3G8). PBMCs were stained with 1000 ng/mL of H2-Db, PG16-Db, or 3BNC117-Db. Data reported as the percentage of cells that stained positive for the indicated scDb (mean, SD) from three replicates. d, Expression of CD16 on peripheral blood lymphocytes, CD3-CD56+ NK cells, CD3+ T cells, and CD19+ B cells. Data reported as the percentage of CD16+ cells (mean, SD) from three replicates.