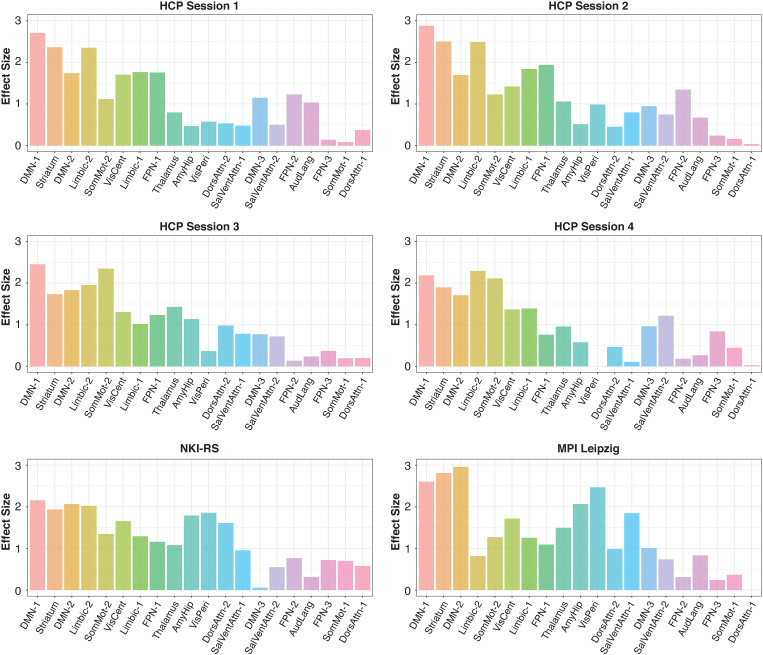
Fig. 6.
Effect size of sex differences in 20 networks across the HCP, NKI-RS, and MPI Leipzig cohorts. Brain networks were ordered based on the ranking of effect sizes across the 4 HCP sessions and the two independent NKI-RS, and MPI Leipzig cohorts. The 20 networks consist of 17 cortical networks (65) and three subcortical networks encompassing the striatum, amygdala–hippocampus, and thalamus (SI Appendix, Table S18). The dorsal default mode network (DMN-1) showed the largest effect size (Cohen’s d > 2) across all networks and cohorts, followed by the striatum and limbic networks (d > 1.5). Rank order: DMN-1 = dorsal default mode network; Striatum; DMN-2 = ventral default mode network; Limbic-2 = limbic network; SomMot-2 = somatomotor network; VisCent = visual central network; Limbic-1 = limbic network; FPN-1 = frontoparietal network; Thalamus; Amy-Hip = amygdala–hippocampus network; VisPeri = visual peripheral network; DorsAttn-2 = dorsal attention network; SalVentAttn-1 = salience/ventral attention network; DMN-3 = default mode network; SAlVentAttn-2 = salience/ventral attention network; FPN-2 = frontoparietal network; AudLang = auditory language network; FPN-3 = frontoparietal network; SomMot-1 = somatomotor network; DorsAttn-1 = dorsal attention network.