Fig. 2.
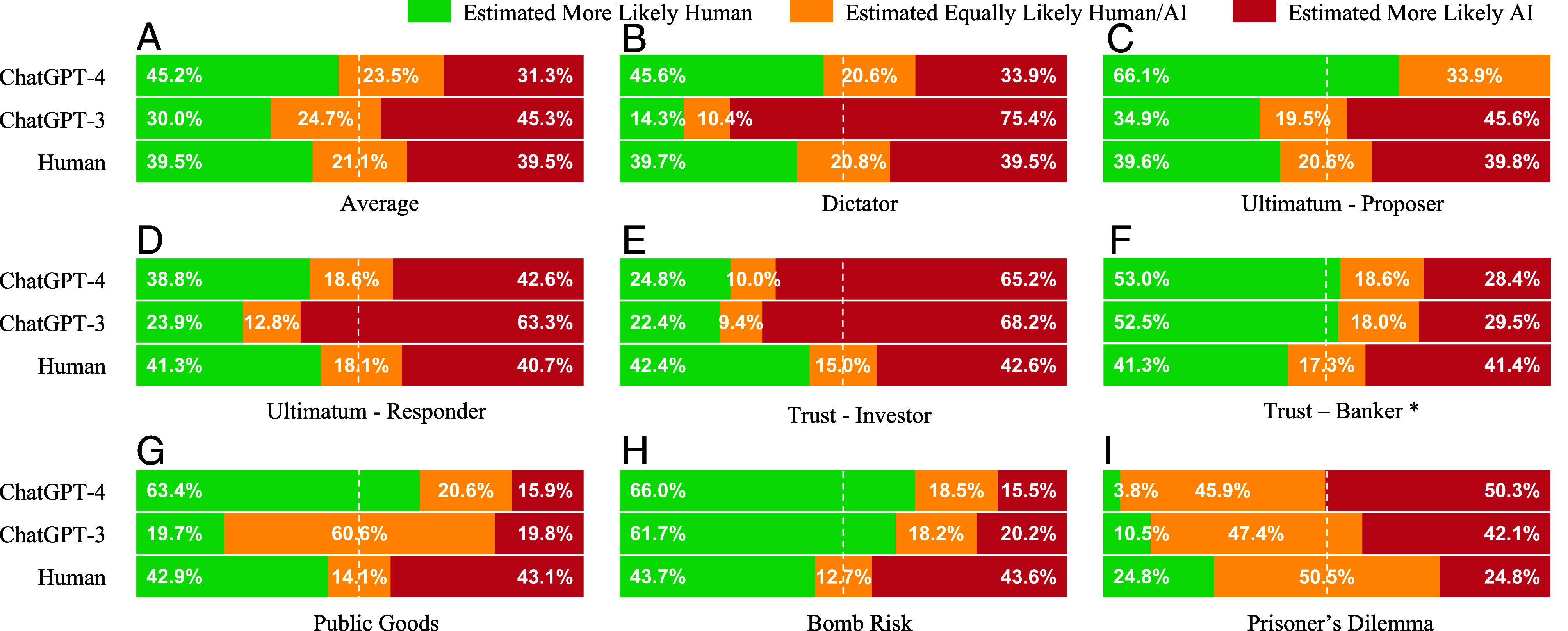
The Turing test. We compare a random play of Player A (ChatGPT-4, ChatGPT-3, or a human player, respectively) and a random play of a second Player B (which is sampled randomly from the human population). We compare which action is more typical of the human distribution: which one would be more likely under the human distribution of play. The green bar indicates how frequently Player A’s action is more likely under the human distribution than Player B’s action, while the red bar is the reverse, and the yellow indicates that they are equally likely (usually the same action). (A): average across all games; (B–I): results in individual games. ChatGPT-4 is picked as more likely to be human more often than humans in 5/8 of the games, and on average across all games. ChatGPT-3 is picked as or more likely to be human more often than humans in 2/8 of the games and not on average.
