Fig. 4.
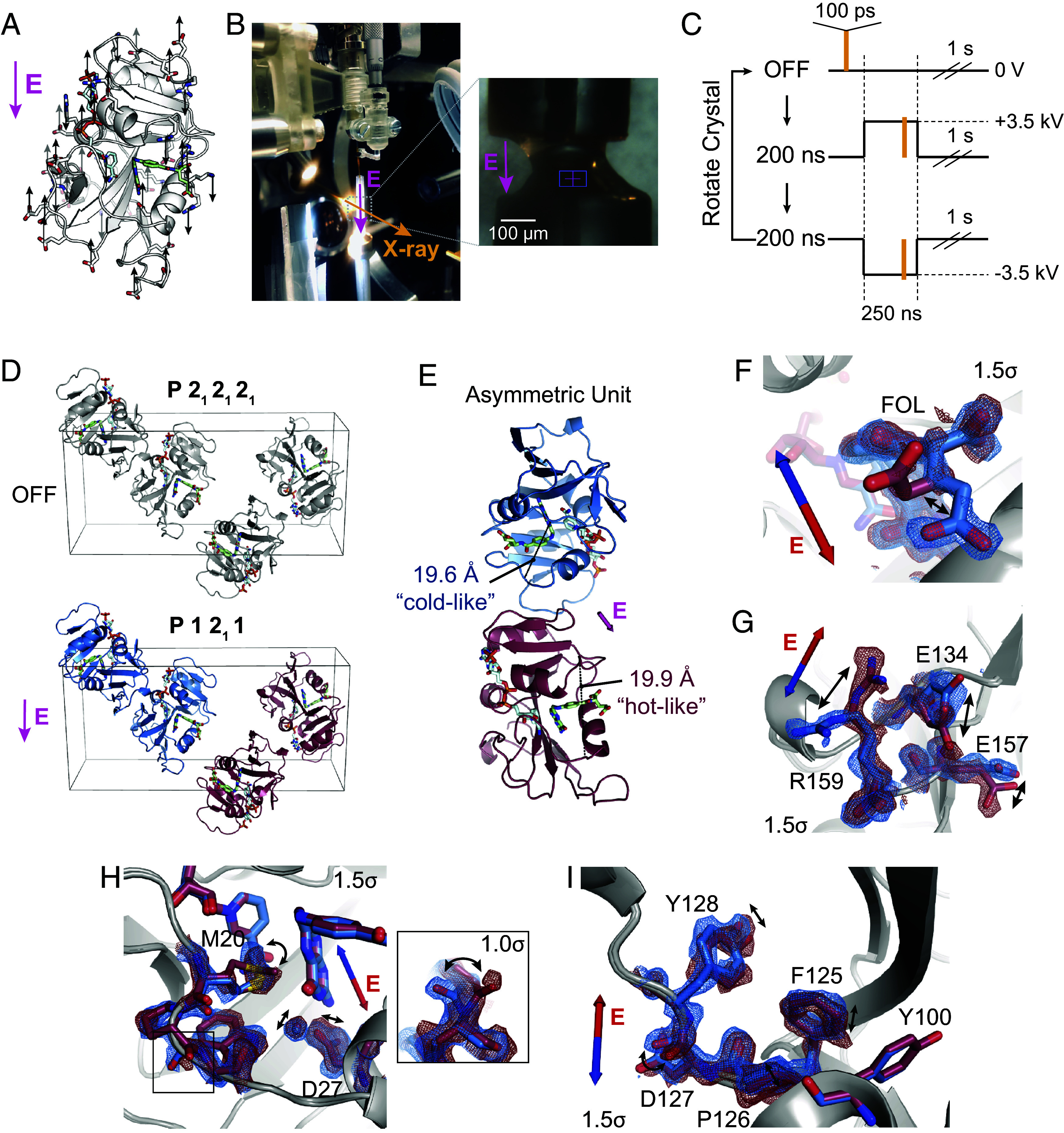
Electric-field-dependent structural changes recapitulate hinge motion and influence on active site residues. (A) Diagram of a possible pattern of force applied by an external electric field (E, in magenta) to ecDHFR based on the distribution of charged residues. (B) Photograph of the experimental apparatus for electric-field-stimulated X-ray crystallography (EF-X) at the BioCARS ID-B beamline; (Inset) zoom-in showing an ecDHFR crystal between two electrodes. (C) Schematic of the data collection strategy, which included three consecutive X-ray pulses at each angle: OFF (no high voltage pulse), 200 ns into a +3.5 kV pulse, and 200 ns into a 3.5 kV pulse. The crystal was rotated after each sequence of three diffraction images in order to collect a complete dataset for each condition. (D) Unit cell of the ecDHFR crystal during the EF-X experiments. During the OFF images, the crystal is in the spacegroup. The applied electric field along the -axis alters the symmetry of the crystal, rendering the crystal in a spacegroup during the high voltage pulses, with two copies in the new asymmetric unit (ASU; copies shown in red and blue). (E) The ASU of the refined excited state model. The two copies in the ASU differ in hinge distance. The different copies of the protein are colored in red and blue as an analogy to the multi-temperature experiment; red represents the expanded active site cleft observed at hotter temperatures, and blue represents the constricted cleft observed at colder temperatures. (F–I) Superposed models and maps from both protein molecules of the excited state ASU highlight electric-field dependent motion of charged groups. Blue and red arrows depict electric field vector for the blue and red models, respectively, and maps are contoured at and carved within 1.5 Å of shown atoms. (F) Carboxylate sidechain of folate and (G) charged sidechains near the C terminus demonstrate electric-field-dependent structural changes consistent with the formal charges of the residues. (H) Active site residues and Pro21 backbone carbonyl (Inset; contoured at ) differ between protein molecules. (I) Conformational changes among residues 125 to 128.
