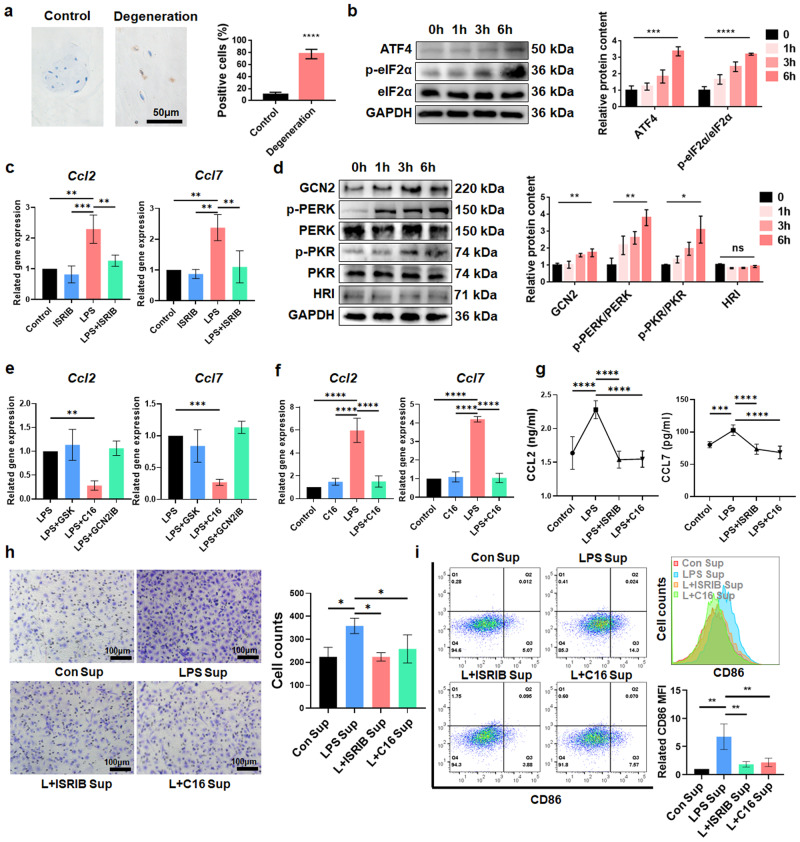
Fig. 4. PKR-mediated ISR is involved in the recruitment and polarization of MΦs during IDD.
a Representative IHC results showing p-eIF2α in degenerated and nondegenerated human NP tissues. b The protein expression of ATF4, p-eIF2α and eIF2α in rNPCs treated with LPS for 6 h was detected by WB analysis. c qPCR results showing CCL2 and CCL7 gene expression in rNPCs after ISRIB pretreatment for 1 h and LPS treatment for 6 h. d The protein expression of ISR-related kinases in rNPCs treated with LPS for 0/1/3/6 h. e qPCR results showing the expression of CCL2 and CCL7 in rNPCs after GSK2606414, PKR-IN-C16 or GCN2iB pretreatment for 1 h and LPS treatment for 6 h. f qPCR results showing CCL2 and CCL7 expression in rNPCs after PKR-IN-C16 pretreatment for 1 h and LPS treatment for 6 h. g ELISA results showing the levels of CCL2 and CCL7 in the supernatant from rNPCs after ISRIB or C16 pretreatment for 1 h and LPS treatment for 6 h. h Transwell assays were used to detect the migration of rMΦs. rMΦs were treated with supernatant extracted from rNPCs that were pretreated with C16 or ISRIB for 1 h and LPS for 6 h. i FCM analysis and quantification of CD68+CD11b+CD86+ or CD68+CD11b+CD206+ rMΦs. Experiments were performed at least 3 times, and the data are presented as the means ± SDs. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant, with ANOVA. Con, control; Sup, supernatant; L, LPS; Bin, bindarit; C16, PKR-IN-C16; GSK, GSK2606414.