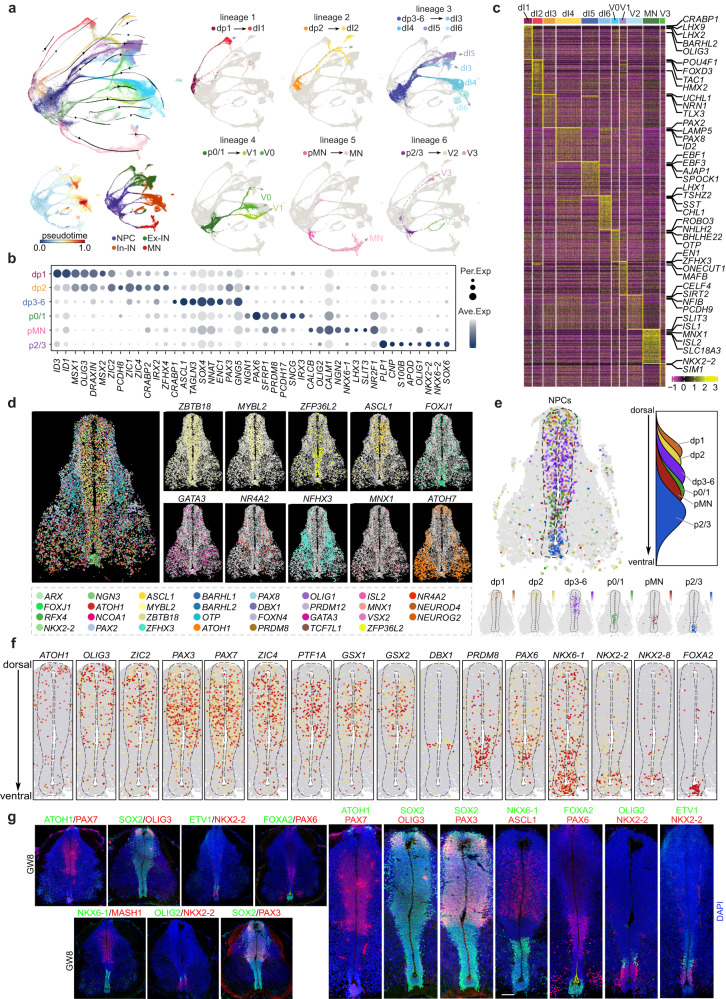
Fig. 2. Molecular and spatial characterization of neural progenitor cells in the developing human spinal cord.
a The distinct neuronal lineages comprising NPCs and neurons are visualized using a UMAP plot that integrates the outcomes of RNA velocity analysis. To enhance clarity, each neuronal lineage is also depicted individually, and illustrated with gray dotted lines. The cells are colored based on their identities as NPCs, Ex-INs, In-INs, and MNs, their pseudotime scores, or based on their identities in different lineages. b The expression profiles of DEGs across diverse NPC subtypes are shown in a dotplot. c A heatmap depicting the expression patterns of DEGs enriched in various neuronal types in the developing human spinal cord is presented. d RNA signals for 31 highly variable genes on a coronal section of the human spinal cord at GW8 are spatially presented, with each dot representing a single molecule of RNA. The spatial expression profiles of some example genes are shown individually for better visualization. e The spatiotemporal arrangement of NPCs along the dorsoventral axis in the VZ of human spinal cord is inferred through an integrated analysis of scRNA-seq and TF-seqFISH data. The spatial distribution of NPC cell types is represented as a simplified density map based on the dorsoventral score. The NPCs are arranged along the DV axis from dorsal to ventral as: dp1, dp2, dp3–6, p0–2, pMN, and p3. f The spatial expression patterns of TFs in the VZ along the dorsoventral axis of the human spinal cord at GW8 are visualized. Each dot represents an individual cell and is colored according to the expression level of the TF (red, high; gray, low). The dotted lines indicate the boundaries of the VZ in the human spinal cord at GW8. g The immunostaining results visualize the spatial expression patterns of TFs, including OLIG3, PAX3, NKX6-1, ASCL1, FOXA2, OLIG2, and NKX2-2, in the VZ of the human spinal cord at GW8. Scale bar, 50 μm.