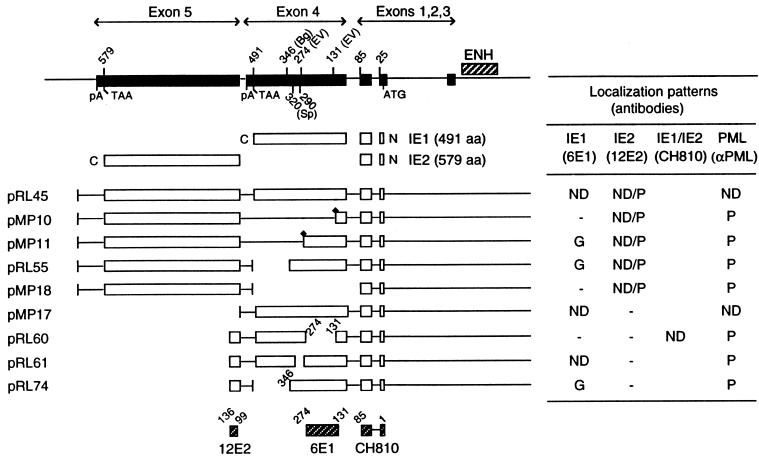
FIG. 3.
Summary of the localization patterns of IE1, IE2, and PML in Vero cells transiently transfected with genomic plasmids expressing deleted versions of IE1. At the top is an illustration of the overlapping five exon structure (solid bar) of the MIE gene transcription unit in the inverted (i.e., viral) genomic orientation. The positions of key restriction sites used to generate the deleted or truncated versions of IE1 are indicated above the diagram. Bg, BglII; EV, EcoRV; Sp, SpeI. The enhancer/promoter region of the MIE locus (ENH; hatched bar) and the translation start (ATG) and termination (TAA) sites as well as polyadenylation sites (pA) are also indicated. Below is a comparison of the structures of the proteins encoded by the variant MIE expression gene plasmids used. Open bars represent coding regions, with gaps denoting in-frame deletions; diamonds indicate inserted triple-terminator oligonucleotides. The estimated map locations for the epitopes recognized by MAbs 6E1, 12E2, and CH810 are shown at the bottom (hatched bars). To detect IE1, IE2, and PML, FITC-labeled MAb 6E1 (for IE1), 12E2 (for IE2), and CH810 (for both IE1 and IE2) were used in double-label IFA experiments together with rhodamine-coupled rabbit PAb against PML. IFA patterns; ND, nuclear diffuse; P, punctate; ND/P, mixture of nuclear diffuse and punctate; G, nuclear granular structures.