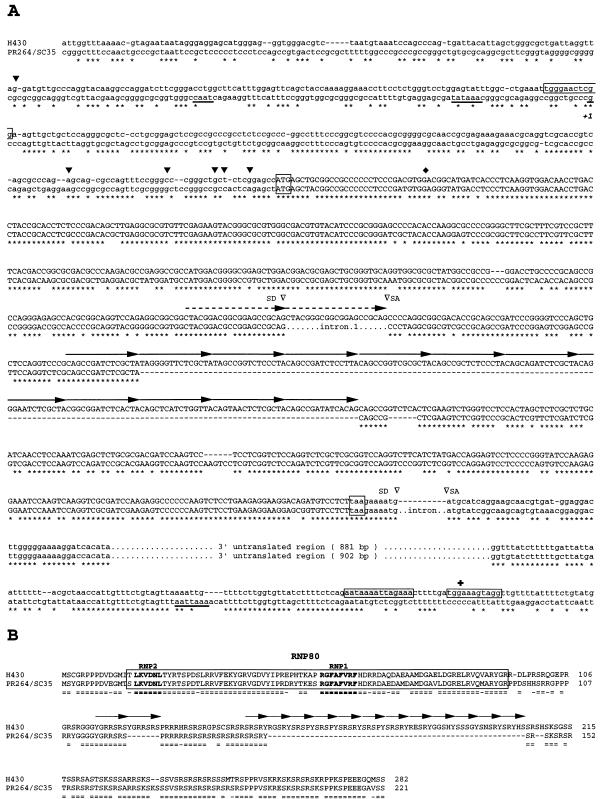
FIG. 3.
Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the human H430 and PR264/SC35 genes. (A) Comparison of H430 and PR264/SC35 nucleotide sequences. Conserved nucleotides are indicated by stars, and gaps have been introduced in order to maximize alignment. The 21-bp duplication found at the junction of the homologous sequences of exons 1 and 2 and the 15-bp degenerate repeats constituting the H430 165-bp insertion are indicated by dashed and solid arrows, respectively. Splice donors (SD), splice acceptors (SA), and introns represented in PR264/SC35 sequences are indicated. The PR264/SC35 CAAT box, the TATA box, the transcription start site (+1), and the polyadenylation signal are underlined. Conserved translation initiation and stop codons are boxed. H430 and PR264/SC35 ORFs are in capital letters. The H430 poly(A) tail remnant and the imperfect repeats flanking the H430 retropseudogene are indicated by shaded and open boxes, respectively. H430 transcript 5′ ends mapped by RACE-PCR experiments are represented by solid arrowheads above the sequence. The H430 cDNA 5′ end (⧫) and polyadenylation site (✚) are indicated. (B) Comparison of H430 and PR264/SC35 amino-acid sequences. Identical amino acids (=) and semiconservative substitutions (-) are indicated. Gaps have been introduced in order to maximize alignment. The RBD is boxed, and the RNP1 and RNP2 motifs are indicated in boldface. YGRRSRS and degenerate SRSRY repeats resulting from the 21-bp duplication and the 165-bp insertion, respectively, are represented by arrows.