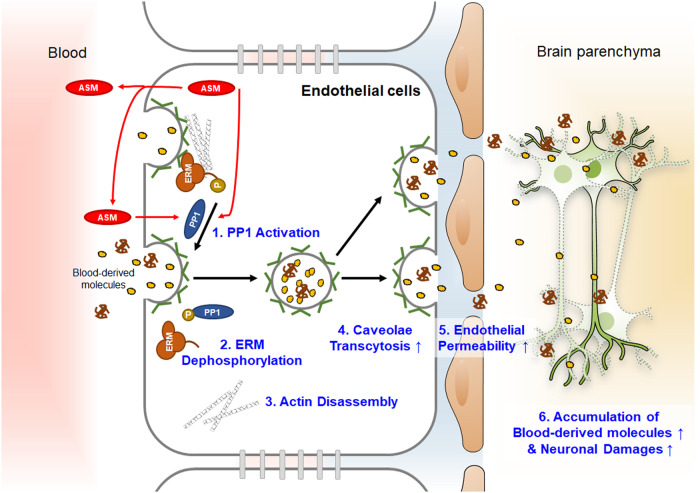
Fig. 2. Brain endothelial cell-derived ASM mediates blood–brain barrier (BBB) disruption in the aged brain.
In the aged brain, ASM activity is strongly increased in the endothelial cells that make up the BBB. Brain endothelial ASM induces PP1-mediated ezrin/radixin/moesin dephosphorylation via autocrine and/or paracrine effects and further causes cytoskeletal disassembly and excessive caveolae internalization. Increased caveolae-mediated transcytosis by ASM results in BBB hyperpermeability and blood-derived molecule extravasation into the brain parenchyma, ultimately leading to neuronal cell death.