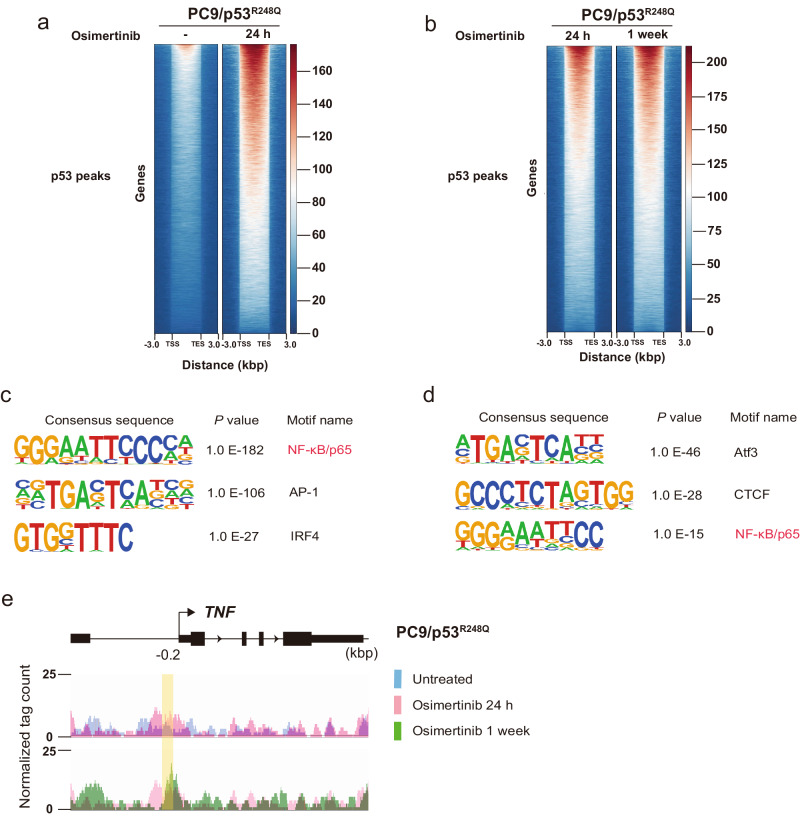
Fig. 5. Osimertinib induces the binding of p53 to p65 binding sites in DNA of PC9/p53R248Q cells.
Aggregation maps of p53 ChIP-seq reads for PC9/p53R248Q cells treated with osimertinib for 0 or 24 h (a) or for 24 h or 1 week (b). Each row shows a region of ±3 kbp centered on a p53 peak, with the rows being rank-ordered on the basis of peak intensity. TSS transcription start site, TES transcription end site. De novo motif analysis for p53 binding peaks enriched in PC9/p53R248Q cells treated with osimertinib for 24 h versus those treated for 0 h (c) as well as in those treated with osimertinib for 1 week versus those treated for 24 h (d). The top three consensus sequences are shown in rank order by p value. e IGV genome browser tracks of ChIP-seq signals for p53 at the TNF gene locus in PC9/p53R248Q cells treated with osimertinib for 0 h (blue), 24 h (pink), or 1 week (green). The y-axis depicts the ChIP-seq signal, and the x-axis the genomic position. The position of the p65 binding motif detected by JASPAR in the promoter region of TNF (−0.2 kbp) as shown in Fig. 4a is highlighted in yellow.