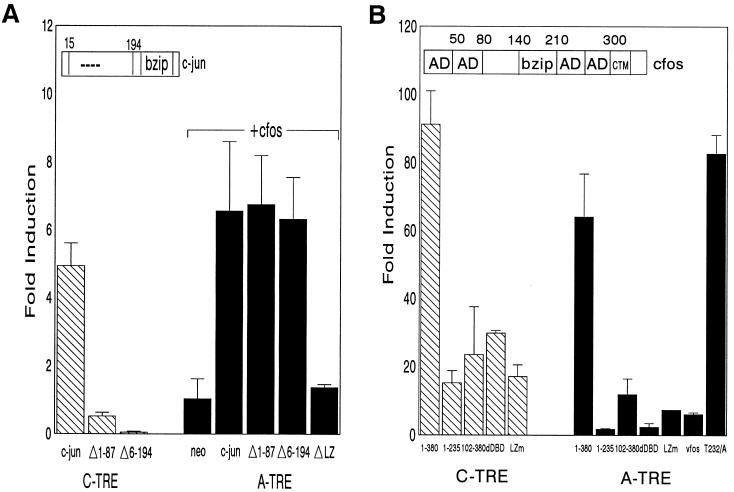
FIG. 3.
The C terminus of c-fos is required for activation of the A-TRE. (A) c-jun activation domains are dispensable for heterodimer induction of the A-TRE. F9 cells were cotransfected with A- and C-TRE (3×) reporter plasmids (3 μg) and expression vectors encoding wild-type c-jun (2.5 μg) alone (5 μg in total, using pRSV-neo), or N-terminally deleted c-jun (2.5 μg), in combination (only for A-TRE) with c-fos vector (2.5 μg). The jun mutants correspond to deletions of amino acids 1 to 87 (MUT1) or 6 to 194 (MUT2), or a deletion in the leucine zipper (LZ) of c-jun (MUT3), respectively. Results are shown as fold induction relative to cells cotransfected with pRSV-neo. (B) Effect of c-fos mutants on heterodimer induction of the TREs. F9 cells were cotransfected with 3× A- or C-TRE plasmid (3 μg) and expression vectors encoding c-jun and full-length c-fos (1-380) or c-fos mutant (5 μg in total). The c-fos mutants correspond to a C-terminal deletion (1-235), an N-terminal deletion (102-380), a deletion in the DBD (dDBD), a mutation in the leucine zipper (LZm), or v-fos, the oncogenic counterpart of c-fos (FBJ-v-fos). Also shown is the result obtained in assays using a mutation of Thr 232 to Ala in c-fos, a site previously shown to be a target for a novel c-fos kinase (17). In the c-fos schematic above the data, AD is used to indicate previously identified activation domains. Fold induction is relative to activity of TREs transfected with pRSV-neo, and the data represent the means of two independent experiments done in duplicate.