FIGURE 6.
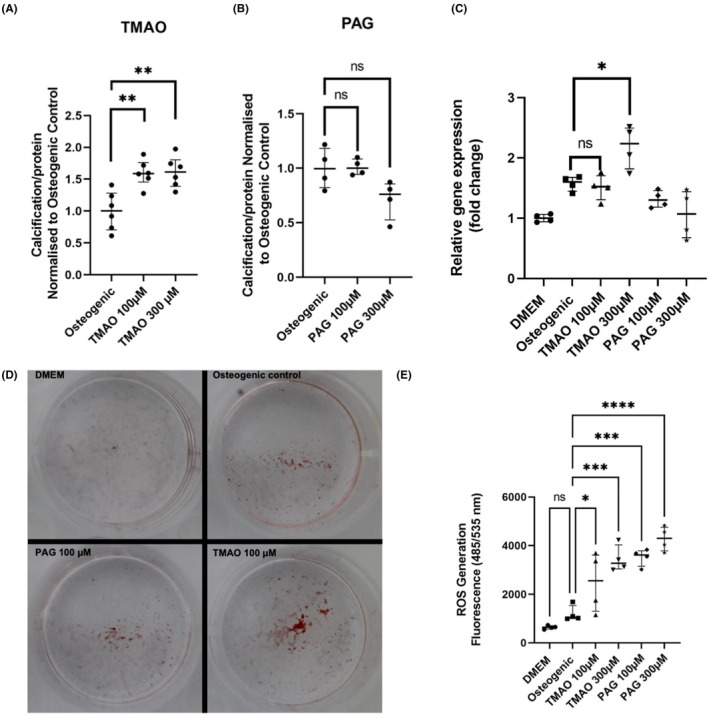
In vitro experiments investigating the effect of TMAO and PAG in VSMC calcification and oxidative stress. (A) TMAO‐induced calcification assay using BoneTag Optical Dye (n = 6 per group). (B) PAG‐induced calcification assay using BoneTag Optical Dye. Aortic VSMCs were incubated with uremic toxins for 7 days in the background of high phosphate (2.5 mM phosphate). For both experiments, readouts were normalised for protein content using BCA assay (n = 4 per group). (C) mRNA expression analysis of osteogenic marker Runx2. Relative gene expression was normalised to DMEM control group (n = 4 per group). (D) Representative images of alizarin red staining for specified conditions. (E) Reactive oxygen species assay for specified conditions using DCFDA/H2DCFDA assay (n = 4 per group). Readout taken 4 h after addition of toxins. Statistics: data presented as mean ± SEM. Groups were compared using one‐way ANOVA followed by group‐wise comparisons using Tukey's post hoc test. p‐values <.05 were deemed statistically significant. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001, ****p < .0001. PAG, phenylacetylglutamine; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TMAO, trimethylamine N‐oxide.
