Figure 4.
ECM niche-dependent AP-1 and TEAD-mediated transcription and the loss of lineage determination synergize to control the fate of cancer cells
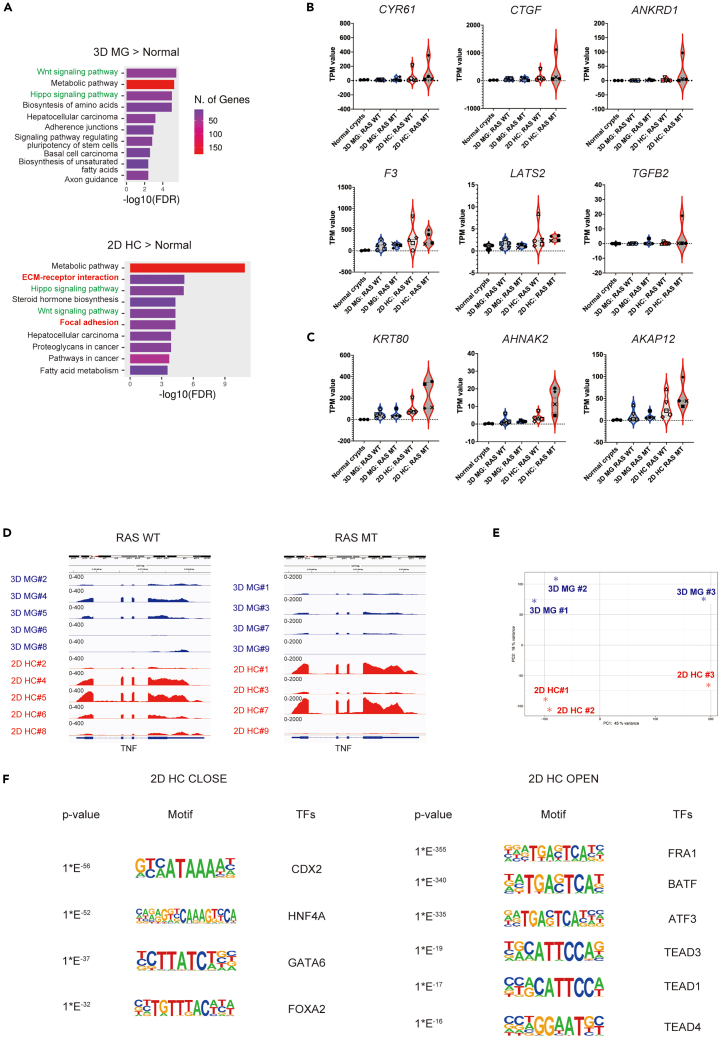
(A) The top 10 KEGG pathway enriched in upregulated genes in nine cultures (#1–9) of 2D HC (left panel) or 3D MG (right panel) compared to normal colonic epithelial crypts in three samples (#1–3) is shown.
(B) Violin plot analyses comparing the distribution of total transcripts per million (TPM) values of indicated genes (CYR61, CTGF, ANKRD1, F3, LATS2, and TGFB2) in nine cultures (#1–9) of 3D MG and 2D HC and three normal colonic epithelial crypts are shown. Samples are subcategorized by RAS mutation status. WT; wild-type, MT; mutation. The color and shape of each point in the cancer cell lines corresponds to each case.
(C) Violin plot analyses comparing the distribution of total transcripts per million (TPM) values of indicated genes (KRT80, AHNAK2, and AKAP12) in nine cultures of 3D MG and 2D HC and three normal colonic epithelial crypts are shown. Samples are subcategorized by RAS mutation status. WT; wild-type, MT; mutation. The color and shape of each point in cancer cell lines correspond to each case.
(D) A representative RNA sequencing track visualized in Integrative Genomic Viewer (IGV) at TNF loci is shown. Samples are subclustered by RAS mutation status. TNF is generally upregulated in 2D HC compared to 3D MG in both RAS wild-type (WT) and RAS mutant (MT) cases. The data range of the RNA sequencing track was set as 400 and 2000 in RAS WT and RAS MT cases, respectively.
(E) A principal component analysis (PCA) plot from the ATAC sequencing analysis (ATAC-seq) of three 3D MG and 2D HC cultures is shown.
(F) Representative motifs among the top 25 most highly enriched transcriptional factor motifs in either 3D MG (2D HCCLOSE) or 2D HC (2D HCOPEN) are shown. See also Figure S3, Tables S2 and S3.