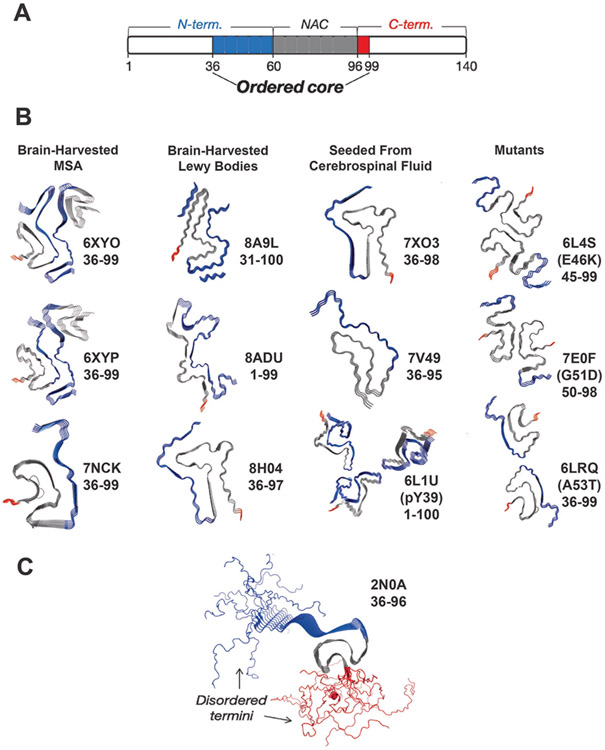
FIGURE 3: The C-terminal domain forms a fuzzy coat on the α-Syn fibril surface.
(a) Schematic of α-Syn domains and their involvement in the fibril core. Monomer domains are defined as shown at the top of the schematic while the fibril structures reveal an ordered core composed mainly of the residues 36-99 of the N–terminal (blue: 36-60) and the NAC region (grey; 60-96). A very small portion of the core is composed of residues from the C-terminal domain (red: 96-99). The rest of the residues (white) are considered disordered in the fibril structure. (b) Cryo-EM structures (PDB IDs provided) of the ordered cores brain-harvested α-Syn fibrils from MSA, brain-harvested α-Syn fibrils from Lewy bodies, α-Syn fibrils seeded from cerebrospinal fluid and mutant α-Syn [36-44] . The ordered cores as captured consist almost exclusively of residues in the N-terminal (blue) and NAC (grey) domains while the C-terminal (red) domain is rarely included. (c) The ssNMR structure of an α-Syn fibril as performed by Tuttle et al [33]. The N-terminal residues are depicted in blue, and the C-terminal residues are depicted in red. The calculated NMR structure reflects the disordered N- and C-termini.