Fig. 3.
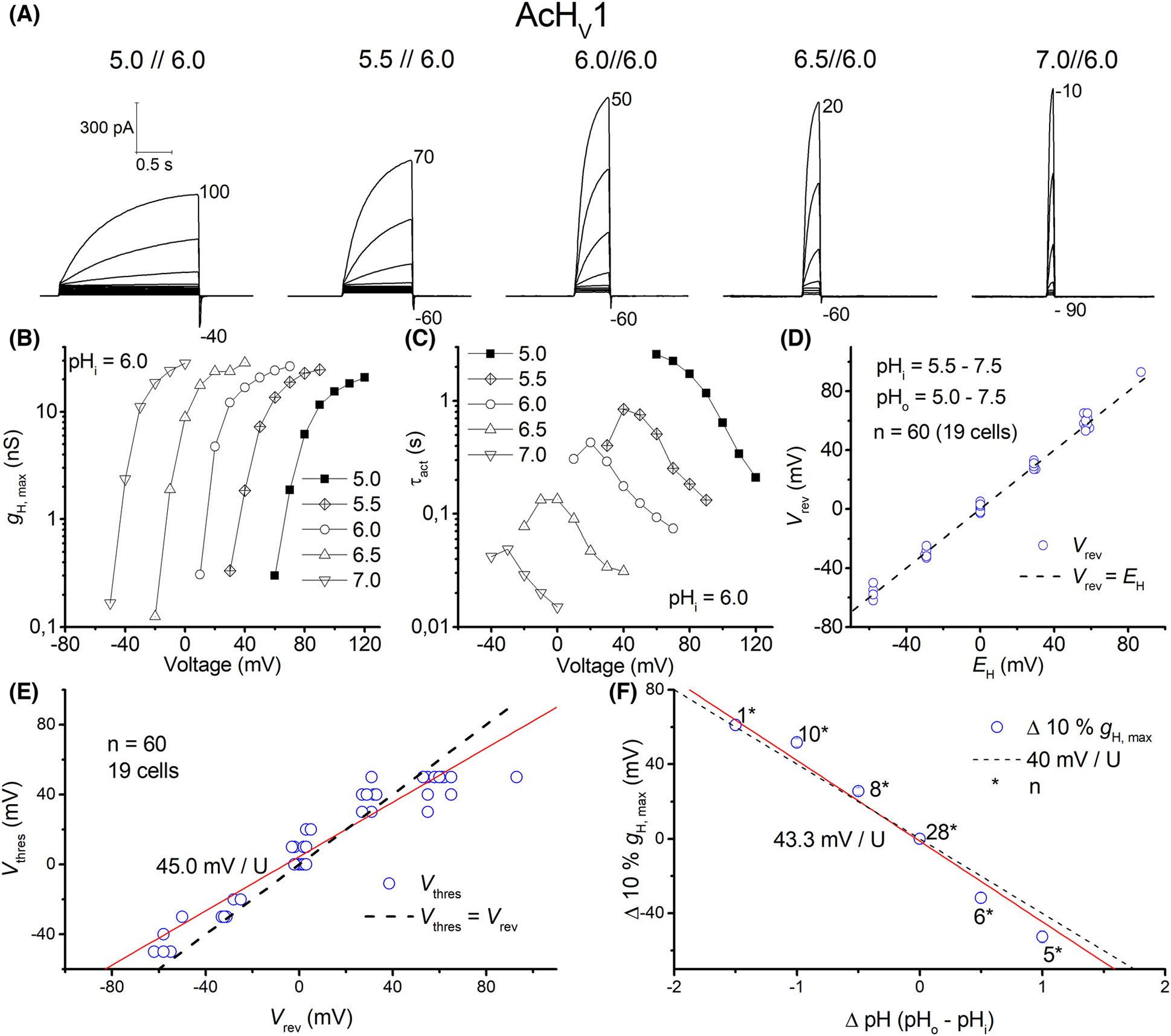
AcHV1 is a typical voltage-gated proton channel. (A) Whole-cell currents in the same cell with pHo ranging from 5–7 at pHi 6.0, in 10 mV increments, pulse length varied with pHo. Holding potential as depicted below the family. (B) Conductance-voltage plot of the current families in (A). (C) Typical speeding of activation kinetics with higher pHo. (D) Reversal potential (Vrev) measurements in 19 cells plotted against EH, showing proton selectivity of AcHV1. (E) Threshold-voltage plot; red line shows changes in Vthres according to Vrev, with a slope 45.0 mV per unit pH. Dashed line shows Vthres equal to Vrev. (F) 10% of maximal conductance vs. voltage shows 43.3 mV shift per unit pH. Dashed line shows the slope of 40 mV per U pH. Numbers with asterisks show number of recordings.
