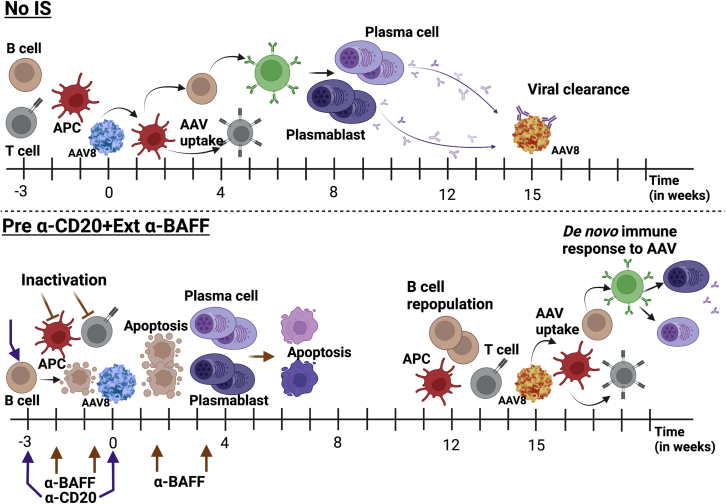
Figure 8.
Proposed mechanism of AAV-specific immune responses in untreated and α-CD20 and α-BAFF-treated animals
AAV8 administration in naive animals without any IS (no-IS) results in AAV uptake, presentation, T cell help, and activation of adaptive immune responses, resulting in the formation of high-titer, affinity-matured AAV capsid-specific Abs, which can prevent vector redosing. IS pretreatment with α-CD20+Ext α-BAFF during initial AAV administration prevents the selection of high-affinity B cell clones and further deprives B cells and plasma cells of the B cell survival cytokine BAFF, thereby enabling vector redosing. The IS effect is transient, and the repopulated B cells initiate a de novo adaptive immune response to the re-administered AAV vector.