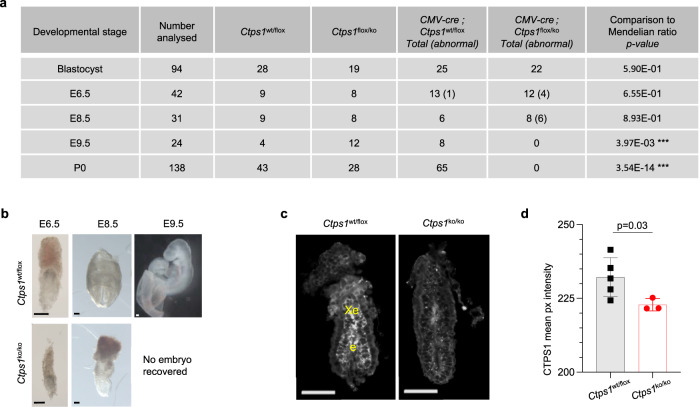
Fig. 1. CTPS1 is essential for embryonic development.
a Quantification of animals with a given genotype at different stages. CMV-Cre; Ctps1wt/ko males were crossed with Ctps1flox/flox females. Blastocysts were generated in vitro. Numbers in brackets indicate abnormal embryos. *** significant difference with a chi-square test, indicating embryonic lethality. b Brightfield images of Ctps1wt/flox (upper panels) and CMV-Cre; Ctps1flox/ko (lower panels) at stage E6.5, E8.5 and E9.5 (Scale bars = 100 µm). Images are representatives of 6–13 embryos analysed in three independent experiments. c Whole mount immunostaining and 3D imaging of E6.5 embryos with an anti-CTPS1 antibody (grey), which is detected in the epiblast (e) and extra-embryonic ectoderm (Xe) in controls Ctps1wt/ko embryos (Scale bars = 100 µm). d The mean pixel intensity of the CTPS1 signal from panel (c) is significantly decreased in CMV-Cre; Ctps1flox/ko mutant embryos. A t-test with Welch’s correction is used and data are presented as the mean ± SD of n = 5 control and three mutant embryos. Source data are provided in Source Data file.