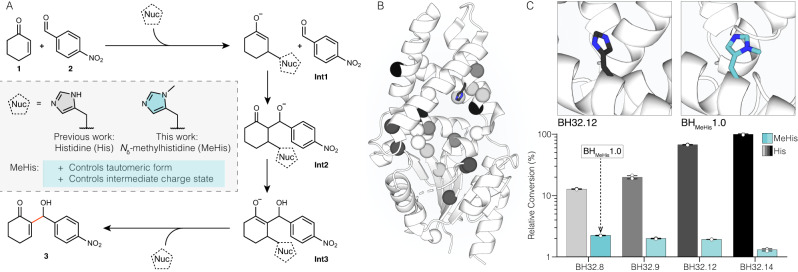
Fig. 1. Investigation of the utility of MeHis as a nucleophile for the MBH reaction and identification of a suitable starting point for directed evolution.
A Chemical scheme for the MBH reaction between 2-cyclohexen-1-one (1) and 4-nitrobenzaldehyde (2) to form MBH product 2-(hydroxy(4-nitrophenyl)methyl)cyclohex-2-en-1-one (3). Previous work has afforded the MBHase BH32.1413 which promotes catalysis via a histidine nucleophile. In this work, His23 is replaced by Nδ-methylhistidine (MeHis) for the creation of a more efficient MBHase. Nuc = nucleophile. B Crystal structure of BH32.12 (PDB: 6Z1L, https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6Z1L) showing the positions of the amino acids mutated during BH32.14 evolution (represented as spheres at the Cα). Mutations are shaded in grey scale according to their order of introduction corresponding to the evolutionary trajectory shown in Fig. 1C. His23 is shown as atom-coloured sticks with black carbon atoms. C The active sites of BH32.12 (PDB: 6Z1L, https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6Z1L) and BHMeHis1.0 (PDB: 8BP1, https://www.rcsb.org/structure/8BP1) are shown with His23 and MeHis23 nucleophiles shown as atom-coloured sticks with black and blue carbon atoms, respectively. Comparisons of activity of BH32.14 and selected variants along the BH32 evolutionary trajectory with either His (grey scale) or MeHis (blue) as the catalytic nucleophile at position 23. BH32.8 His23MeHis (subsequently referred to as BHMeHis1.0) was selected for further engineering. Biotransformations were performed using 1 (15 mM), 2 (1.5 mM) and enzyme (60 µM) in PBS (pH 7.4) with 3% (v/v) MeCN as cosolvent and analyzed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) following 5 h incubation at 30 °C. Error bars represent the standard deviation of measurements made in triplicate centred around the averaged value. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.