FIGURE 6.
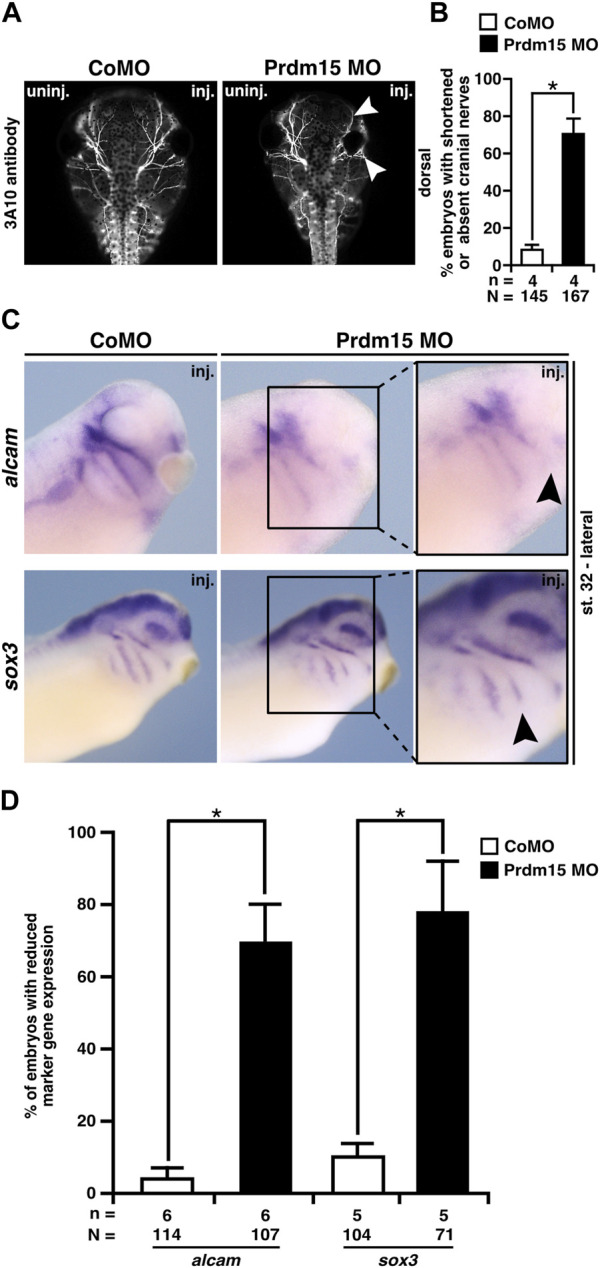
Prdm15 MO injection hinders proper development of the cranial nerves and placodes. (A) Dorsal views of control MO-injected and Prdm15 MO–injected embryos show a shortened or decreased branching of cranial nerves (white arrowheads) upon Prdm15 KD visualized by 3A10 antibody staining. (B) Statistical evaluation of embryos with shortened or absent branching of cranial nerves as illustrated in (A). (C) Lateral view of stage 32 embryos reveals a reduction (black arrowheads) of the respective expression upon Prdm15 MO KD in both marker genes of the lateral placodes (alcam and sox3) using whole-mount in situ hybridization. (D) Statistical evaluation of alcam and sox3 expression revealed a significant reduction in its expression upon Prdm15 KD as illustated in (C). Abbreviations: alcam, activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule; inj., injected; MO, morpholino oligonucleotide; n, number of independent experiments; N, number of analyzed embryos in total; Prdm15, PR-domain zinc finger protein 15; sox3, SRY-box transcription factor 3; uninj., un-injected. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means. *, p ≤ 0.05.
