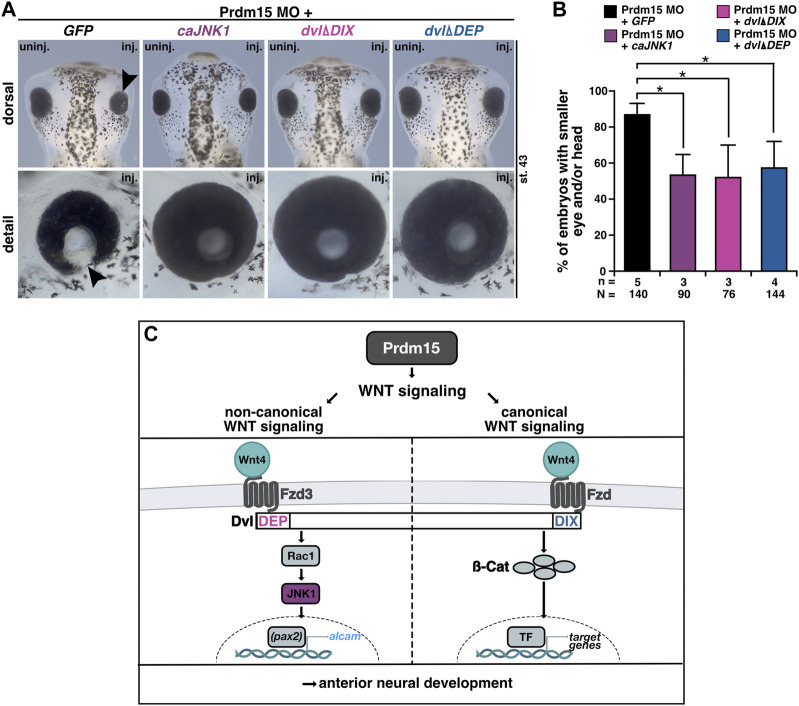
FIGURE 9.
Prdm15 influences canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling upstream of Wnt4. (A) Dorsal and detailed view of stage 43 embryos injected with Prdm15 MO in combination with GFP RNA or the constitutive active JNK1 (caJNK1) RNA or the two different mutated disheveled versions (dvlΔDIX, dvlΔDEP). The co-injection of Prdm15 MO with caJNK1 and the dvlΔDIX-mutated version as well as the dvlΔDEP-mutated version shows rescue of the severe Prdm15 MO–induced phenotype in contrast to the negative control GFP (black arrowhead). (B) Statistical evaluation of embryos with smaller eye or head as described in (A) shows a rescue with caJNK1, dvlΔDIX, and dvlΔDEP RNA. (C) Schematic overview of Prdm15 and WNT signaling. Prdm15 acts upstream of Wnt4 and influences the expression of wnt4 and alcam through the non-canonical WNT/PCP signaling pathway possibly via the transcription factor pax2. Furthermore, the canonical Wnt signaling pathway is also affected downstream of Prdm15. Abbreviations: alcam, activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule; ß-cat, β-catenin; caJNK1, constitutive active JNK 1; DEP, disheveled Egl-10 and pleckstrin; DIX, disheveled Axin; dvl, disheveled; Fzd, frizzled; Fzd3, frizzled3; GFP, green fluorescent protein; inj., injected; JNK1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1; MO, morpholino oligonucleotide; n, number of independent experiments; N, number of analyzed embryos in total; pax2, paired box 2; Prdm15, PR-domain zinc finger protein 15; Rac1, Rac1 family small GTPase 1; st., stage; TF, transcription factor; uninj., un-injected; WNT, wingless-type MMTV integration site family member; wnt4, wnt family member 4. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means. *, p ≤ 0.05.