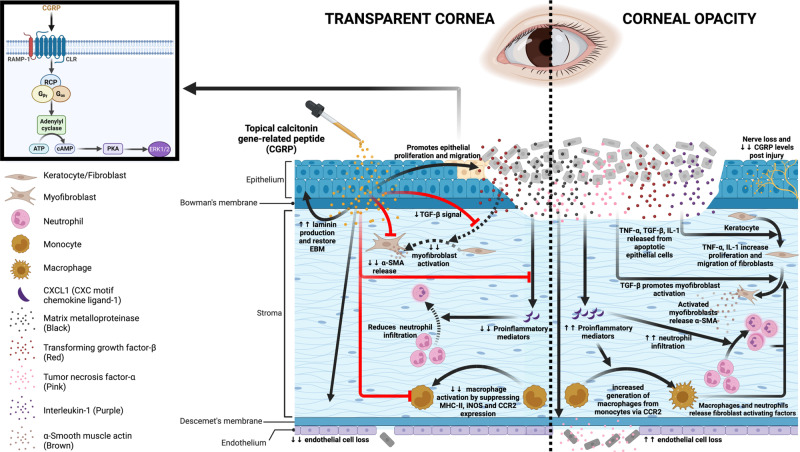
Fig. 8. Schematic showing the effects of CGRP on corneal wound healing after mechanical injury.
Injury leads to nerve damage and a decrease in CGRP level in the cornea. Topical application of CGRP promotes corneal epithelial cell regeneration and restores the epithelial basement membrane, thus reducing the release of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic mediators including TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-1, and CXCL1 into the stroma. This leads to reduced keratocyte activation and stromal fibrosis. In addition, CGRP reduces neutrophil infiltration, macrophage maturation, and the production of inflammatory cytokines. It reduces corneal endothelial cell loss and maintains its pump function. Clinically, topical application of CGRP as an eye drop accelerates epithelial closure, preserves transparency, and prevents scar formation and edema after corneal injury. The figure was created with BioRender.com.