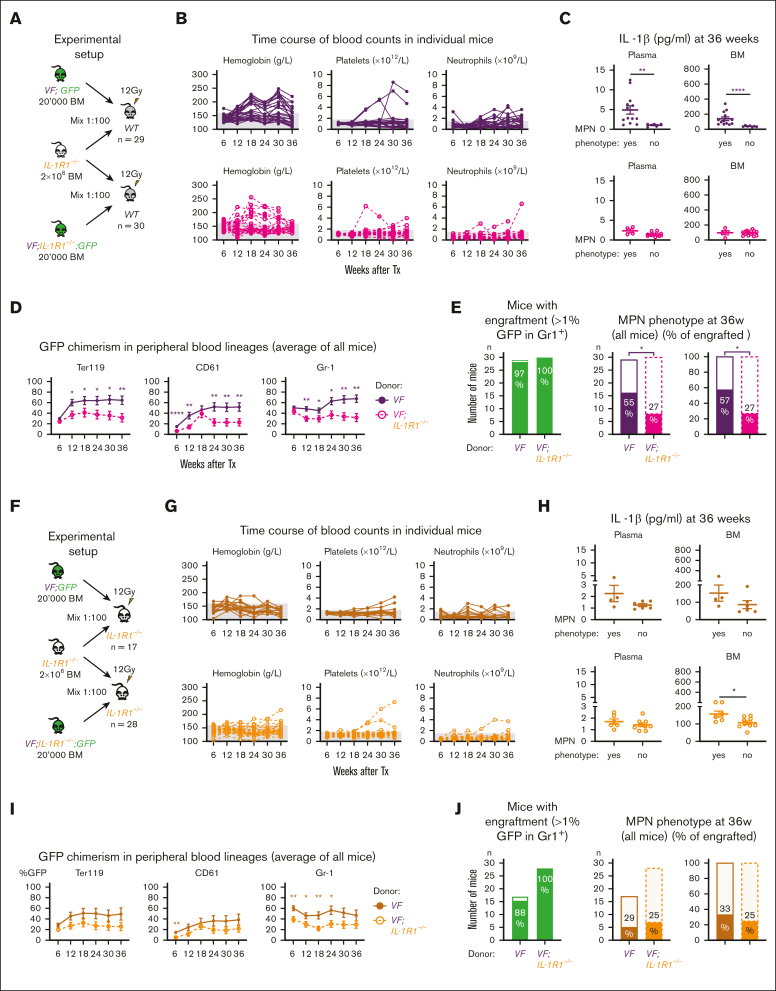
Figure 3.
JAK2-mutant cells need IL-1R1 expression on both hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells for optimal MPN initiation. (A) Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for competitive transplantation at 1:100 dilution. BM from VF;GFP or VF;IL-1R1−/−;GFP donor mice was mixed with a 100-fold excess of BM competitor cells from an IL-1R1−/− donor. (B) Time course of blood counts from individual mice that received BM from VF;GFP (upper panel) or VF;IL-1R1−/−;GFP donors (lower panel). (C) IL-1β protein levels in plasma and BM lavage (1 femur and 1 tibia) of mice with or without MPN phenotype is shown. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney 2-tailed t test was performed for statistical comparisons. (D) GFP chimerism in the peripheral blood. Multiple t tests were performed for statistical analyses. (E) Bar graphs show the percentages of mice that showed engraftment defined as GFP chimerism of >1% at 18 weeks after transplantation and the percentages of mice that developed MPN phenotype (elevated hemoglobin and/or platelet counts). P values in lower panel were computed using Fisher exact test. (F-J) Schematic drawing of the identical aforementioned experiment, in which IL-1R1−/− mice were used as the recipients instead of WT mice. Annotations as in panels B through E. Gray shaded area represents normal range. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. See also supplemental Figures 5 and 6.