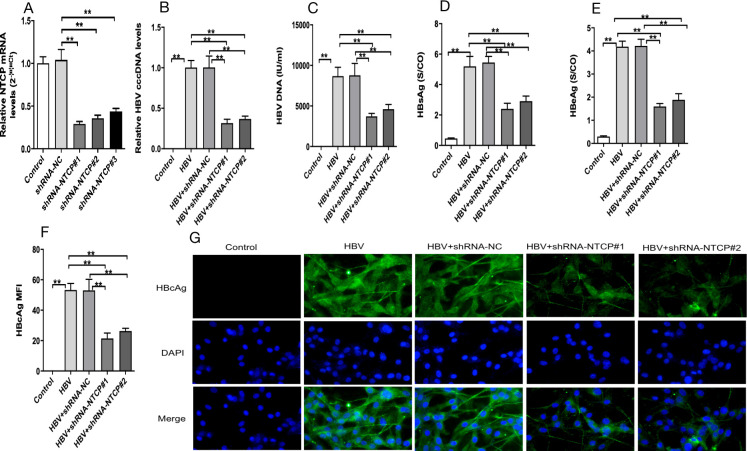
Fig 2.
Effect of NTCP downregulation and NTCP blockade on HBV-infected HPCs. Differentiated podocytes were transfected with shRNA-NC, shRNA-NTCP#1, or shRNA-NTCP#2 by lentiviral plasmid, and the expression of NTCP measured by qPCR was significantly downregulated after transfection with shRNA-NTCP (A) HPCs in the HBV, HBV + shRNA-NC (a control plasmid), shRNA-NTCP#1, and shRNA-NTCP#2 groups were incubated with HepG 2.2.15 supernatant (containing HBV) for 16 h, with HPCs incubated with cell culture medium as the control. The levels of HBV cccDNA (B) and HBV DNA (C) were measured by qPCR. The levels of HBsAg (D) and HBeAg (E) in the supernatant from the indicated groups were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (F, G) Representative images of HBcAg (green) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) nuclear (blue) staining in differentiated human podocytes. The levels of HBV cccDNA (B), HBV DNA (C), HBsAg (D), HBeAg (E), and HBcAg (F, G) were significantly decreased after downregulating or inhibiting NTCP. Scale bar = 200 µm. Results are mean ± SD for three individual experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.