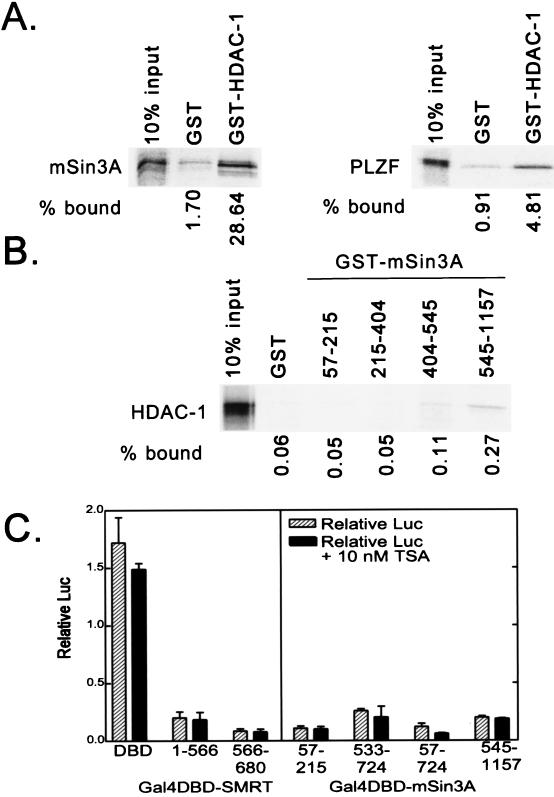
FIG. 4.
Interaction of HDAC-1 with mSin3A and effects of trichostatin A on repression. (A) Binding of mSin3A to GST–HDAC-1. Full-length, radiolabeled mSin3A was synthesized in vitro by a coupled transcription-translation protocol. The radiolabeled mSin3A protein was then incubated with nonrecombinant GST (used as a negative control) or a GST fusion of HDAC-1, each expressed in bacteria and immobilized on a glutathione column. Radiolabeled mSin3A protein bound to the immobilized proteins was eluted with soluble glutathione, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized and quantified by PhosphorImager analysis (left panel). The percentage of HDAC-1 bound to GST or to GST-HDAC-1 is depicted below the panel and was determined relative to the total radiolabeled mSin3A used in the assay (input). A parallel experiment using radiolabeled PLZF as a positive control for interaction with HDAC-1 is also presented (right panel). (B) Binding of HDAC-1 to GST-mSin3A. An experiment reciprocal to that in panel A was performed, using radiolabeled, full-length HDAC-1 and GST fusions representing various portions of mSin3A (as indicated above the lanes). Radiolabeled HDAC-1 protein bound to the different GST-mSin3A fusion constructs was eluted, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized and quantified by PhosphorImager analysis, as described for panel A. (C) Lack of effect of trichostatin A on SMRT-mSin3A-mediated transcriptional repression. Various GAL4-DBD fusions representing the silencing domains of SMRT and mSin3A, as indicated below each panel, were transfected into CV-1 cells together with an SV40 late promoter (GAL4 17-mer) luciferase reporter in the presence or absence of 10 nM trichostatin A (TSA), an inhibitor of HDAC activity. The cells were harvested 48 h later, and the expression of the luciferase reporter, relative to that of the pCH100 internal control, was determined (“Relative Luc”). The results presented represent the averages and standard deviations obtained from at least two duplicate experiments.