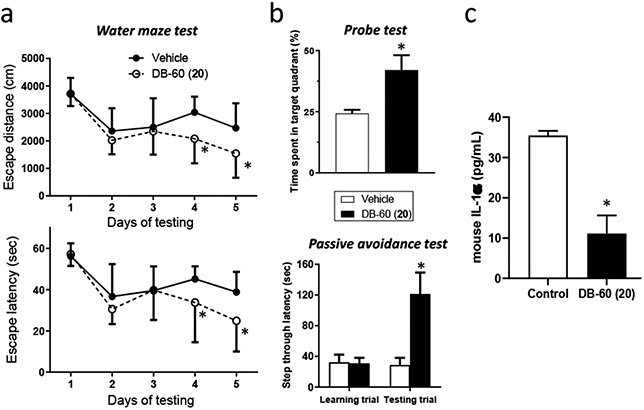
FIGURE 5.
(a) DB-60 (20) improves cognitive function in Tg2576 mice. The Morris water maze test was performed to measure cognitive function: escape distance (upper) and escape latency time (lower). Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA. *Difference in days 4-5 between control and DB-60 (20)-treated mice was statistically significant (p-value < 0.05, n=12 for control and n=5 for DB-60 (20)-treated mice). (b) The probe trial (on day 6, upper panel) and passive avoidance test (on days 7-8, lower panel) were performed following the Morris water maze test on days 1-5. The student’s t-test was used for statistical analyses of probe trials and passive avoidance. Differences in time spent in target quadrant or step through latency between control and DB-60 (20)-treated mice were statistically significant (p-value < 0.05, n=5). (c) Serum samples collected from mice treated with vehicle or DB-60 (20) were used to quantify IL-1α levels via ELISA (p-value <0.05, n=3).