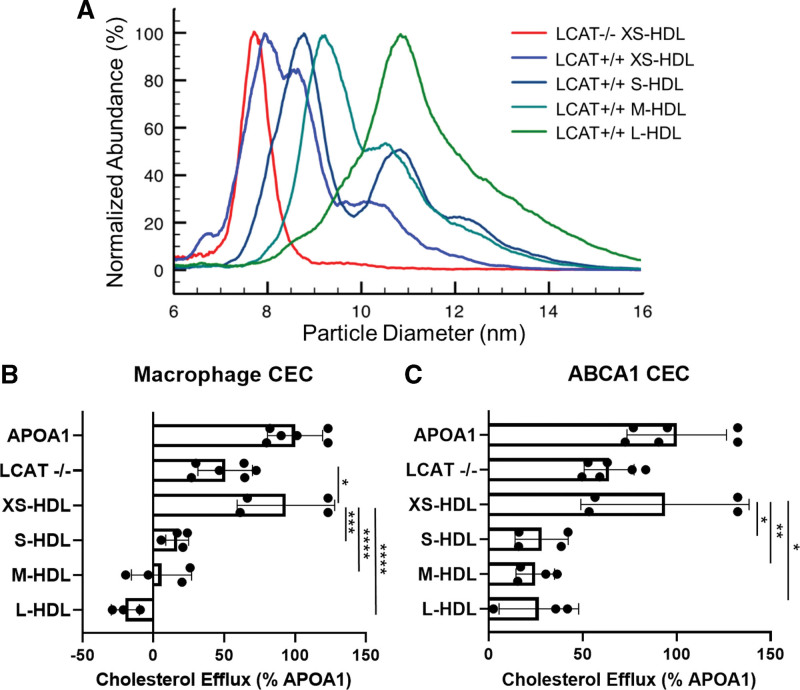
Figure 5.
Calibrated IMA (A) and CEC (B) of HDL isolated from plasma of LCAT-deficient (LCAT-/-) and control (XS-HDL, S-HDL, M-HDL, and L-HDL) subjects. A, Representative IMA size profiles of isolated HDL. To facilitate comparison of size distributions of the particles, the height of each isolated HDL fraction was set to 100%. The diameters of the isolated HDLs of LCAT-/- subjects and control subjects were as follows: LCAT-/-, 7.8±0.1 nm; XS-HDL, 8.1±0.2 nm; S-HDL, 8.8±0.1 nm; M-HDL, 9.8±0.2 nm; and L-HDL, 11.1±0.2 nm. Note that isolated XS-HDL is composed of both XS-HDL and S-HDL particles. B and C, ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC) of HDL isolated from LCAT-/- subjects and control subjects. Macrophage CEC and ABCA1 CEC were quantified with [3H]cholesterol-labeled J774 macrophages and baby hamster kidney cells after a 4-hour incubation. Expression of ABCA1 was induced with cAMP and mifepristone, respectively. Cholesterol efflux was calculated as the percentage of radiolabel in the medium of the cells divided by the total radioactivity of the medium and cells. CEC was quantified as the difference in cholesterol efflux of cells with and without induced expression of ABCA1. Isolated HDLs were included in the media of the cells at equal particle concentrations. CEC of HDLs was normalized to CEC of cells exposed to 10 µg/mL of APOA1 (apolipoprotein A1). P value: 1-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post-tests. ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, and *P<0.05. ABCA1 indicates ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; IMA, ion mobility analysis; LCAT, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase; L-HDL, large HDL; M-HDL, medium HDL; S-HDL, small HDL; and XS-HDL, extra-small HDL.