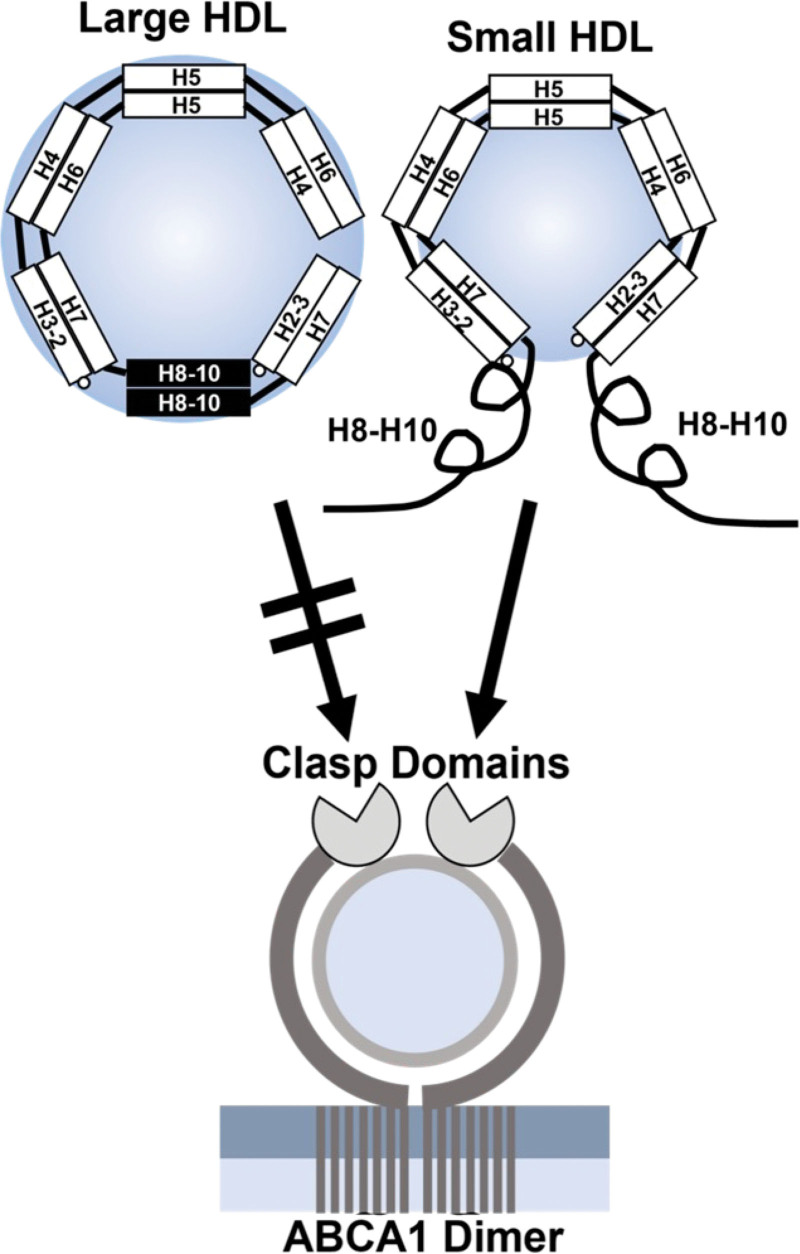
Figure 7.
The “flipped ends” model for the increased ABCA1 activity of small HDLs. In large HDL particles, the C-termini of the APOA1 dimer are in antiparallel helical bundles that are amphipathic and strongly associated with lipid. In small HDL particles, the reduced surface area and high surface curvature force the C-termini off the particles, increasing their mobility. The termini also are less lipid-associated because APOA1 loses its amphipathic double-belt structure. Decreased lipid association and increased mobility of the C-termini (helices H8–H10) promote the engagement of APOA1 with the clasp domains of ABCA1, stimulating cholesterol export from the cell. An alternative hypothesis is that the C-termini of APOA1 promote microsolubilization of phospholipids and cholesterol from phospholipid-rich domains in the plasma membrane of cells (see Discussion). ABCA1 indicates ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; APOA1, apolipoprotein A1; and HDL, high-density lipoprotein.